-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
_SKU_FIT0450__Micro_DC_Motor_with_Encoder SJ01_带编码器直流减速电机
DFRobot新款微型直流减速电机,专为机器人DIY爱好者设计,减速比高达120:1。带两相正交霍尔编码器输出,单圈可输出16个脉冲信号。配合减速箱,单圈可输出高达1920个脉冲信号。配合Arduino控制器和电机驱动器或者直接使用RoMeo主控器就能够完成闭环PID控制、测速、PWM调速等功能。 电机采用纯铜输出轴,内嵌螺纹,加强的连接接头,极大的延长电机的使用寿命,连接也更加方便。搭配我们的移动平台,您可以非常方便的实现速度和方向的精确控制。
- 齿轮齿数比:120:1
- 无负载转速(6V):160rpm
- 无负载转速(3V):90rpm
- 电机最大无负载电流(6V):170mA
- 电机最大无负载电流(3V):140mA
- 最大堵转电流:2.8A
- 最大输出力矩(6V):0.8kgf.cm
- 编码器电压:4.5~7.5V
- 电机工作电压:3~7.5V(额定电压6V)
- 额定力矩:0.2kgf.cm
- 操作环境温度:-10~+60℃
| | |
| ----------------------------------------------------------- | |
| | |
|

| 标号 | 名称 | 功能描述 |
| 1 | 电机电源引脚+ | 3-7.5V,额定电压6V |
| 2 | 电机电源引脚- | |
| 3 | 编码器A相输出 | 随电机转速的变化输出频率变化的方波 |
| 4 | 编码器B相输出 | 随电机转速的变化输出频率变化的方波(接中断口) |
| 5 | 编码器电源GND | |
| 6 | 编码器电源正极 | 4.5-7.5V |
-
硬件
- DFRduino UNO x1
- 直流电源 x1
- L298电机驱动板 x1
-
软件
- Arduino IDE 点击下载Arduino IDE
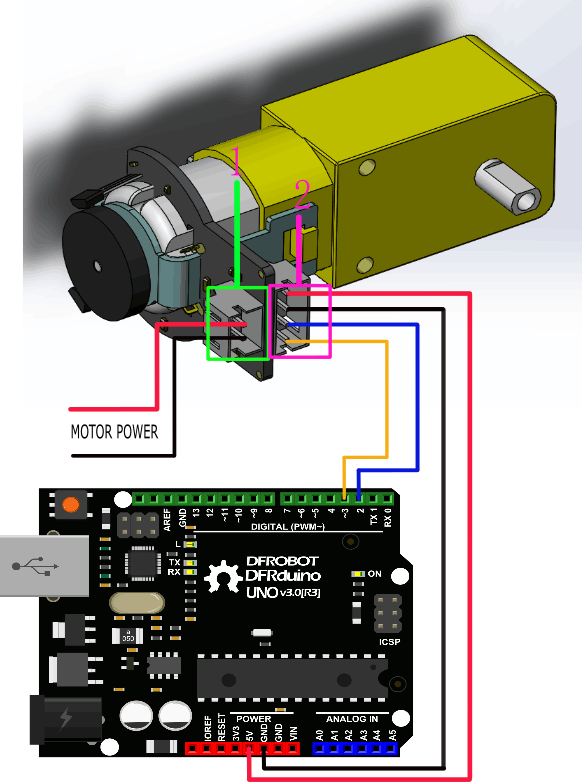
本次教程意在编码器的使用上,选用D2和D3两个管脚,其中D2作为了中断口,D3作为信号输入引脚。在实际应用中只需要确保两个管脚中有一个必须是中断管脚即可,另一个可自行定义(参见下图主控的中断管脚)
Notcie: attachInterrupt() 
详细情况请查看 http://arduino.cc/en/Reference/AttachInterrupt
示例代码1:
//The sample code for driving one way motor encoder
const byte encoder0pinA = 2;//A pin -> the interrupt pin 0
const byte encoder0pinB = 3;//B pin -> the digital pin 3
byte encoder0PinALast;
int duration;//the number of the pulses
boolean Direction;//the rotation direction
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(57600);//Initialize the serial port
EncoderInit();//Initialize the module
}
void loop()
{
Serial.print("Pulse:");
Serial.println(duration);
duration = 0;
delay(100);
}
void EncoderInit()
{
Direction = true;//default -> Forward
pinMode(encoder0pinB,INPUT);
attachInterrupt(0, wheelSpeed, CHANGE);
}
void wheelSpeed()
{
int Lstate = digitalRead(encoder0pinA);
if((encoder0PinALast == LOW) && Lstate==HIGH)
{
int val = digitalRead(encoder0pinB);
if(val == LOW && Direction)
{
Direction = false; //Reverse
}
else if(val == HIGH && !Direction)
{
Direction = true; //Forward
}
}
encoder0PinALast = Lstate;
if(!Direction) duration++;
else duration--;
}
代码1运行现象:
说明:数据不断的从串口输出,当电机正转时,输出的数值>0, 电机反向转时,输出数字<0。并且电机速度越快,数字的绝对值越大,反之越小。
示例代码2(PID控制): 通过L298P直流电机驱动板驱动直流电机,PID算法控制电机的转速。
- 电机电源口连接至L298电机驱动M1口
- 下载并安装Arduino PID库。 如何安装库?
//The sample code for driving one way motor encoder
#include <PID_v1.h>
const byte encoder0pinA = 2;//A pin -> the interrupt pin 0
const byte encoder0pinB = 3;//B pin -> the digital pin 3
int E_left =5; //L298P直流电机驱动板的使能端口连接到数字接口5
int M_left =4; //L298P直流电机驱动板的转向端口连接到数字接口4
byte encoder0PinALast;
double duration,abs_duration;//the number of the pulses
boolean Direction;//the rotation direction
boolean result;
double val_output;//用于提供给电机PWM功率值。
double Setpoint;
double Kp=0.6, Ki=5, Kd=0;
PID myPID(&abs_duration, &val_output, &Setpoint, Kp, Ki, Kd, DIRECT);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);//Initialize the serial port
pinMode(M_left, OUTPUT); //L298P直流电机驱动板的控制端口设置为输出模式
pinMode(E_left, OUTPUT);
Setpoint =80; //设置PID的输出值
myPID.SetMode(AUTOMATIC);//设置PID为自动模式
myPID.SetSampleTime(100);//设置PID采样频率为100ms
EncoderInit();//Initialize the module
}
void loop()
{
advance();//电机正转
abs_duration=abs(duration);
result=myPID.Compute();//PID转换完成返回值为1
if(result)
{
Serial.print("Pluse: ");
Serial.println(duration);
duration = 0; //计数清零等待下次计数
}
}
void EncoderInit()
{
Direction = true;//default -> Forward
pinMode(encoder0pinB,INPUT);
attachInterrupt(0, wheelSpeed, CHANGE);
}
void wheelSpeed()
{
int Lstate = digitalRead(encoder0pinA);
if((encoder0PinALast == LOW) && Lstate==HIGH)
{
int val = digitalRead(encoder0pinB);
if(val == LOW && Direction)
{
Direction = false; //Reverse
}
else if(val == HIGH && !Direction)
{
Direction = true; //Forward
}
}
encoder0PinALast = Lstate;
if(!Direction) duration++;
else duration--;
}
void advance()//电机正转
{
digitalWrite(M_left,LOW);
analogWrite(E_left,val_output);
}
void back()//电机反转
{
digitalWrite(M_left,HIGH);
analogWrite(E_left,val_output);
}
void Stop()//电机停止
{
digitalWrite(E_left, LOW);
}
代码2运行现象:
因为程序设定的PID值为80,所以电机会稳定转速在80左右,当外界的力量(比如电机的驱动电压变化,电机受到的阻力变大等)迫使转速改变时,程序会通过PWM调节,使转速稳定在80左右。比如增大电机驱动电压,电机转速会短暂的上升后下降到80,减小电机驱动电压,电机转速会短暂下降后,上升到80。