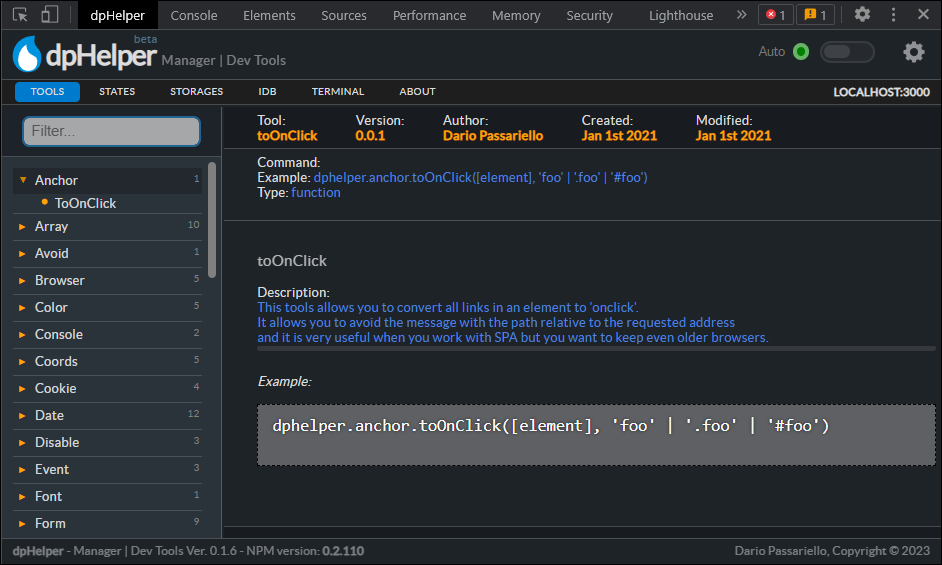
Manager | DevTools by Dario Passariello (c)
dpHelper is a precise and complete collection of 190+ tools ready to use in all web/SaaS applications. State and Store Management are now easy and global, accessible everywhere in your application, including Ajax or React apps, without the need for extra files or Redux setup.
import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
import 'dphelper';
function App() {
// Store a value in the state
state.test = 'Hello, World!';
// Use the stored value in a React component
useEffect(() => {
console.log("You can recall from all pages: " + state.test); // Output: "Hello, World!"
}, []);
return (
<div>
<h1>{state.test}</h1>
</div>
);
}
export default App;You can see an HTML version where dpHelper and LayerPro work together seamlessly. dpHelper is compatible with a variety of frontend libraries, including:
- HTML
- React
- Vue
- And any other frontend library
You can see:
You can see more tutorials, information, and examples about dpHelper clicking here.
dpHelper is primarily designed to work with websites, SPA, SaaS applications, and portals that use AJAX/XMLHttpRequest technology, such as:
- PWA (Progressive Web Apps)
- SPA (Single-Page Applications)
- SaaS
- Microservice
and more...
It is also indicated to work with and for:
- React
- jQuery
- Angular
- Vue
- Vanilla
and more...
Modern browsers and applications use a "NO REFRESH" behavior, where only the affected parts of the page are re-rendered, rather than reloading the entire page. This can cause data loss when refreshing or reloading the page.
If you want to use dpHelper as a data manager, consider using the store function in a non-AJAX engine. If you need help or more information, feel free to contact me.
You can use the state function to store and reuse data throughout your application. Similar to other state managers, you can save state information in JSON format and access it easily in various contexts, including React useEffect and/or dispatch.
For example, you can store a value like this: state.test = 'I am ready' and then retrieve it later using state.test.
example:
You can use the browser's devtools console and type " state.test = 'I am ready' ". Every time you want to use 'test' values, you need just recall state.test.
// Set a state
state.test = "I am ready";
// Get the state
state.test
// List all states
state.list // or just "state" to see the proxy
// Remove a state
state.remove("test")Note: Observer works only with states. Stores are excluded at the moment.
🔥NEW🔥: Great, now you can use nested objects in observer. You need to declare "state." or "store." before selecting the object you want to monitor.
If you want to run a function every time a state changes, you can use:
/**
* Observer is a non-cumulative listener,
* triggered from customEvent / dispatch from state
* @parameters
* [ state | store, function ]
*/
observer( "state.test", () => alert("Test Changes to: " + state.test) )
|__________| |___________________________________________|
State: string Function
PS: you need to use the name of state | store as stringYou can use it everywhere. Works like "useState" in React but with more flexibility (use one observer for each state!).
import 'dphelper';
// Use the observer to log the changing state value
observer(
'state.count',
() => console.log("State changed: ", state.count)
);
// Store a value in the state that changes every 5 seconds
setInterval(() => state.count = Date.now(), 5000);import 'dphelper';
// Set a state
state.myData = 'Hello, world!';
// Retrieve the state
console.log(state.myData); // Output: Hello, world!
// Observe state changes
observer('myData', () => {
console.log('myData has changed to:', state.myData);
});
// Change the state
state.myData = 'New value';When using dpHelper for permanent storage, you should use the store, which stores data persistently across sessions.
-
Use store for persistent storage: If you want to store data permanently, use store to ensure it is saved in localStorage.
-
Remove data when necessary: To maintain security, remove stored data when it is no longer needed, such as during logout.
-
Clear all stored data: Use store.clearAll() to securely remove all stored data from your application.
// Set a store:
store.set("test", { test: "test" })
// Get a store:
store.get("test") // Output: { test: "test" }
// Remove a store:
store.delete("test") // Output: "ok"
// Remove all stores:
store.clearAll() // Output: "ok"import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
import 'dphelper';
function App() {
// Store a value in the store (persistent storage)
store.set(
'user',
{
name: 'John Doe',
age: 30
}
);
// Use the stored value in a React component
useEffect(
() => {
console.log(store.get("user")); // Output: { name: "John Doe", age: 30 }
$("#name").text(store.get("user").name)
}, []
);
// Clear all stored data if necessary
// store.clearAll();
return (
<div>
<h1 id="name">...</h1>
</div>
);
}
export default App;Install dpHelper.
npm i dphelper --save-devor update:
npm i dphelper@latest --save-devUse it in the main root file (and only there):
import "dphelper";or
require("dphelper");Note: You don't need to use npm install in this case, or you will get an error.
<script src="https://unpkg.com/dphelper@latest/index.js"></script>Type dphelper in the devtool console of your browser to have a look at all available tools that you can use! You can call these from everywhere without import (just one time in the main/root page).
Chrome: Download from Google Web Store
Edge: Download from Microsoft Addons
PS: dpHelper is compatible with all Chromium-based browsers like Brave too!
The dpHelper browser extension allows you to manage your application's dpHelper NPM. Key features include:
- Simplified API operations: Easily manage and manipulate data with dpHelper's collection of scripts.
- Real-time monitoring: Track memory usage and localStorage to optimize your application's performance.
- Stay up-to-date: Receive updates and tips to improve your daily workflow.
- Easy installation: Simply import 'dphelper' in your project index to get started.
- Global accessibility: All scripts are available globally and can be accessed from anywhere in your application.
MIT - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIT_License
Dario Passariello - [email protected], All rights reserved - Copyright (c) 2019 - 2024