- Pull the all related docker images :
docker pull docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:8.13.4
docker pull docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:8.13.4
docker pull docker.elastic.co/logstash/logstash:8.13.4- Write the Docker Compose file :
version: '3.7'
services:
# The 'setup' service runs a one-off script which initializes users inside
# Elasticsearch — such as 'logstash_internal' and 'kibana_system' — with the
# values of the passwords defined in the '.env' file. It also creates the
# roles required by some of these users.
#
# This task only needs to be performed once, during the *initial* startup of
# the stack. Any subsequent run will reset the passwords of existing users to
# the values defined inside the '.env' file, and the built-in roles to their
# default permissions.
#
# By default, it is excluded from the services started by 'docker compose up'
# due to the non-default profile it belongs to. To run it, either provide the
# '--profile=setup' CLI flag to Compose commands, or "up" the service by name
# such as 'docker compose up setup'.
setup:
profiles:
- setup
build:
context: setup/
args:
ELASTIC_VERSION: ${ELASTIC_VERSION}
init: true
volumes:
- ./setup/entrypoint.sh:/entrypoint.sh:ro,Z
- ./setup/lib.sh:/lib.sh:ro,Z
- ./setup/roles:/roles:ro,Z
environment:
ELASTIC_PASSWORD: ${ELASTIC_PASSWORD:-}
LOGSTASH_INTERNAL_PASSWORD: ${LOGSTASH_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}
KIBANA_SYSTEM_PASSWORD: ${KIBANA_SYSTEM_PASSWORD:-}
METRICBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD: ${METRICBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}
FILEBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD: ${FILEBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}
HEARTBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD: ${HEARTBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}
MONITORING_INTERNAL_PASSWORD: ${MONITORING_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}
BEATS_SYSTEM_PASSWORD: ${BEATS_SYSTEM_PASSWORD:-}
networks:
- elk
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
elasticsearch:
build:
context: elasticsearch/
args:
ELASTIC_VERSION: ${ELASTIC_VERSION}
volumes:
#- ./elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml:ro,Z
- elasticsearch:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data:Z
ports:
- 9200:9200
- 9300:9300
environment:
node.name: elasticsearch
ES_JAVA_OPTS: -Xms512m -Xmx512m
# Bootstrap password.
# Used to initialize the keystore during the initial startup of
# Elasticsearch. Ignored on subsequent runs.
ELASTIC_PASSWORD: ${ELASTIC_PASSWORD:-}
# Use single node discovery in order to disable production mode and avoid bootstrap checks.
# see: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/bootstrap-checks.html
discovery.type: single-node
networks:
- elk
restart: unless-stopped
logstash:
build:
context: logstash/
args:
ELASTIC_VERSION: ${ELASTIC_VERSION}
volumes:
#- ./logstash/config/logstash.yml:/usr/share/logstash/config/logstash.yml:ro,Z
- ./logstash/pipeline:/usr/share/logstash/pipeline:ro,Z
ports:
- 5044:5044
- 50000:50000/tcp
- 50000:50000/udp
- 9600:9600
environment:
LS_JAVA_OPTS: -Xms256m -Xmx256m
LOGSTASH_INTERNAL_PASSWORD: ${LOGSTASH_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}
networks:
- elk
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
restart: unless-stopped
kibana:
build:
context: kibana/
args:
ELASTIC_VERSION: ${ELASTIC_VERSION}
#volumes:
# - ./kibana/config/kibana.yml:/usr/share/kibana/config/kibana.yml:ro,Z
ports:
- 5601:5601
environment:
KIBANA_SYSTEM_PASSWORD: ${KIBANA_SYSTEM_PASSWORD:-}
networks:
- elk
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
restart: unless-stopped
networks:
elk:
driver: bridge
volumes:
elasticsearch:
- Start your deployment without 'Setup' service (manual deployment) :
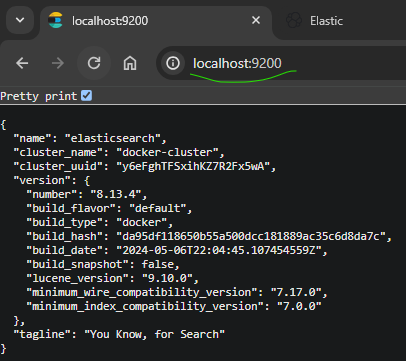
docker compose up- Test the Elastic node via browser :
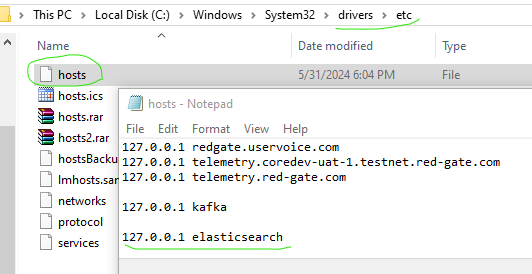
- Add elasticsearch DNS A record within etc/hosts :
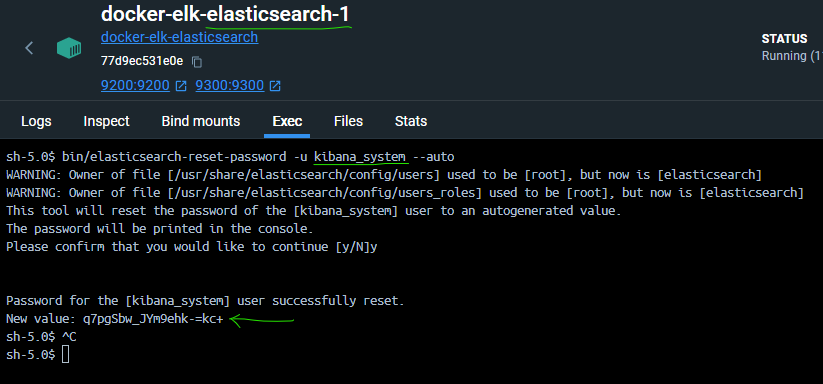
- On the elasticsearch node, write the below command :
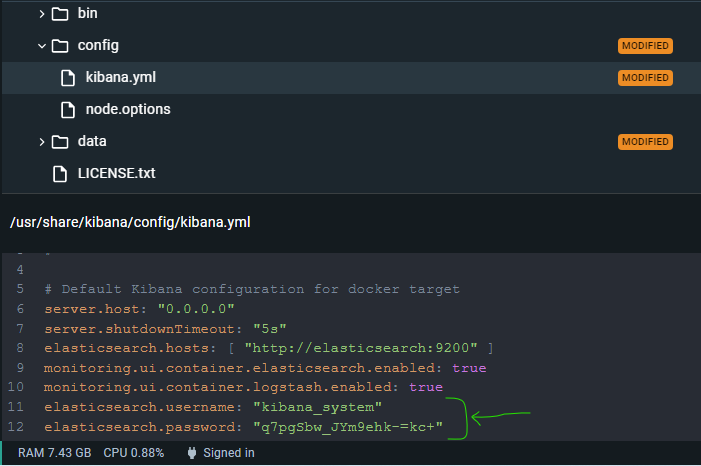
bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u kibana_system --auto- And copy the New Value result to the kibana node and kibana.yml :
elasticsearch.username: "kibana_system"
elasticsearch.password: "q7pgSbw_JYm9ehk-=kc+"
- And go to the kibana portal :
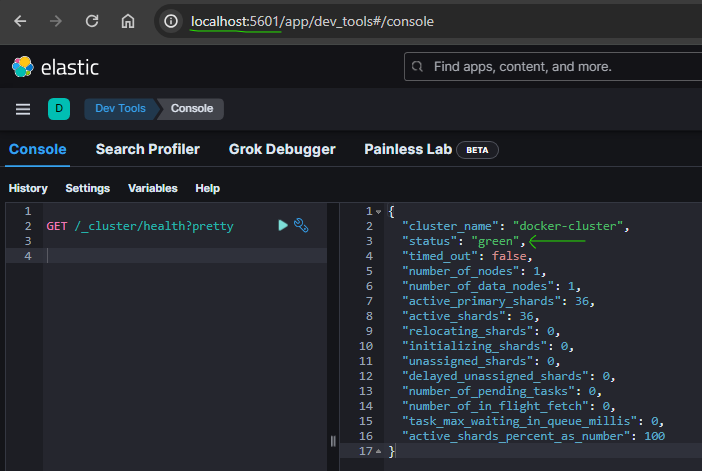
- Get the elastic node healthy info from kibana :
GET /_cluster/health?pretty
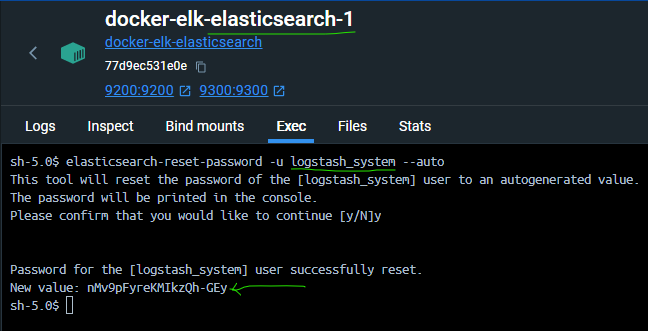
- On the elasticsearch node, write the below command :
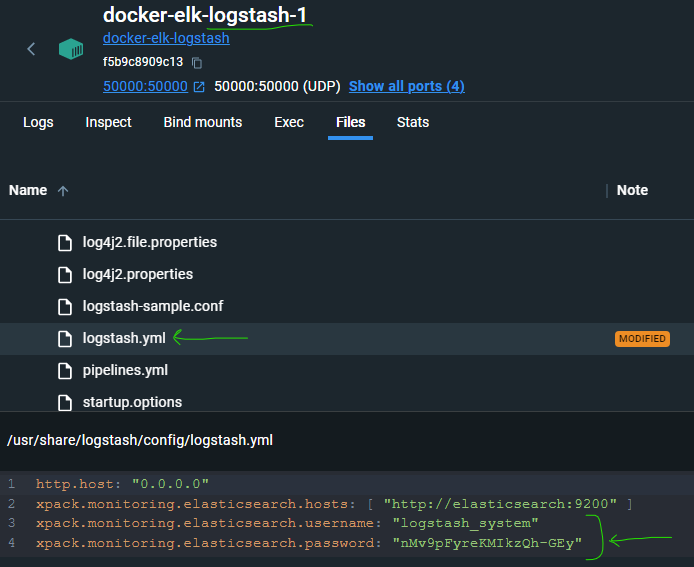
bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u logstash_system --auto- Copy the New Value result to the logstash node and logstash.yml :
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.username: "logstash_system"
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.password: "nMv9pFyreKMIkzQh-GEy"
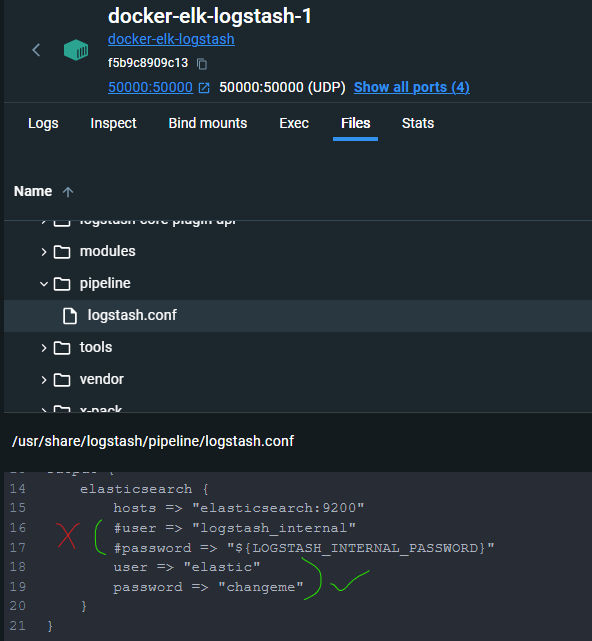
- Then change the elastic node auth info in the logstash.conf :
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "elasticsearch:9200"
#user => "logstash_internal"
#password => "${LOGSTASH_INTERNAL_PASSWORD}"
user => "elastic"
password => "changeme"
}
}
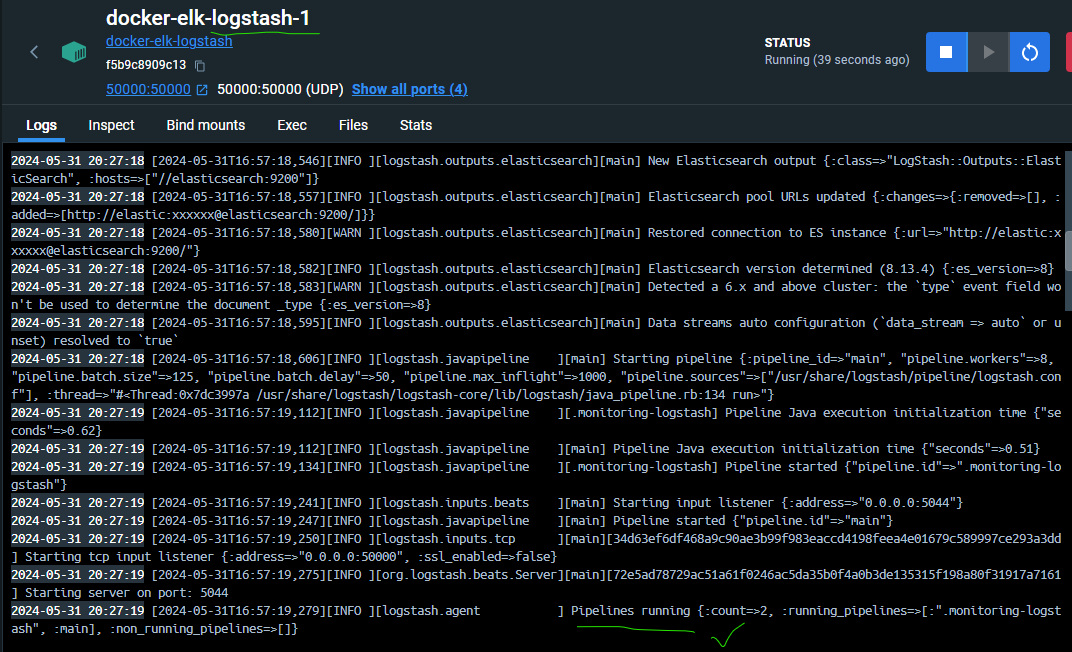
- Check the logstash log :
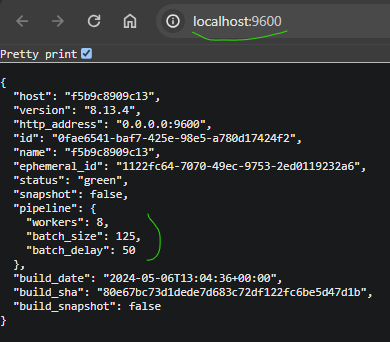
- And logstash info :
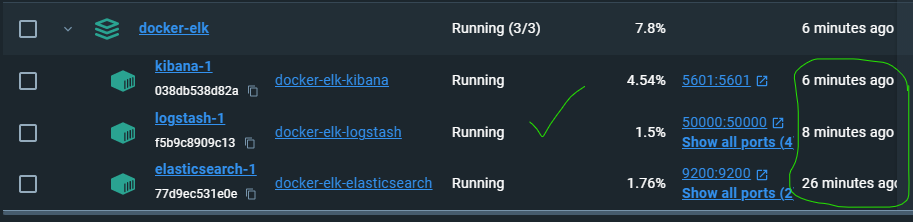
- And the docker desktop shows that stack is healthy :
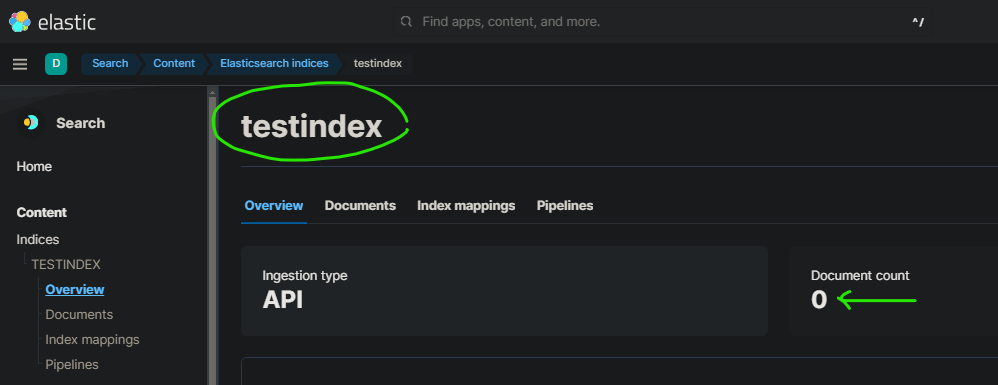
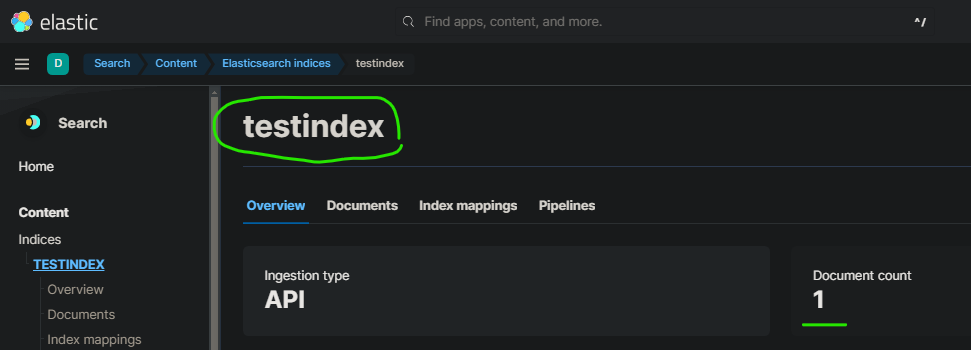
- Create your index named testindex in elasticsearch via kibana :
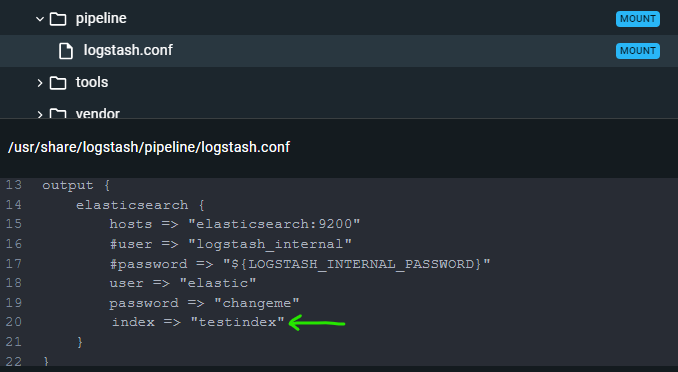
- Add below lines at logstash.conf :
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "elasticsearch:9200"
#user => "logstash_internal"
#password => "${LOGSTASH_INTERNAL_PASSWORD}"
user => "elastic"
password => "changeme"
index => "testindex"
}
}
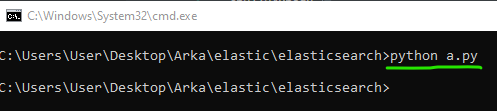
- Write some python scripts or C# code for sending data to the related port (50000) :
import socket
import sys
HOST = '192.168.1.4'
PORT = 50000
try:
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
except socket.error as msg:
sys.stderr.write("[ERROR] %s\n" % msg[1])
sys.exit(1)
try:
sock.connect((HOST, PORT))
except socket.error as msg:
sys.stderr.write("[ERROR] %s\n" % msg[1])
sys.exit(2)
msg = '{"id":"1","name":"kayvan soleimani","email":"[email protected]}'
sock.send(msg.encode('utf-8') )
sock.close()
sys.exit(0)C# Code :
using System;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
string HOST = "192.168.1.4";
int PORT = 50000;
try
{
using (Socket sock = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp))
{
sock.Connect(HOST, PORT);
string msg = "{\"id\":\"2\",\"name\":\"Sorayya Asadi\",\"email\":\"[email protected]\"}";
byte[] data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(msg);
sock.Send(data);
Console.WriteLine("Data sent to logstash ...");
}
}
catch (SocketException ex)
{
Console.Error.WriteLine($"[ERROR] {ex.Message}");
Environment.Exit(1);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.Error.WriteLine($"[ERROR] {ex.Message}");
Environment.Exit(2);
}
Console.ReadLine();Then run the python script :
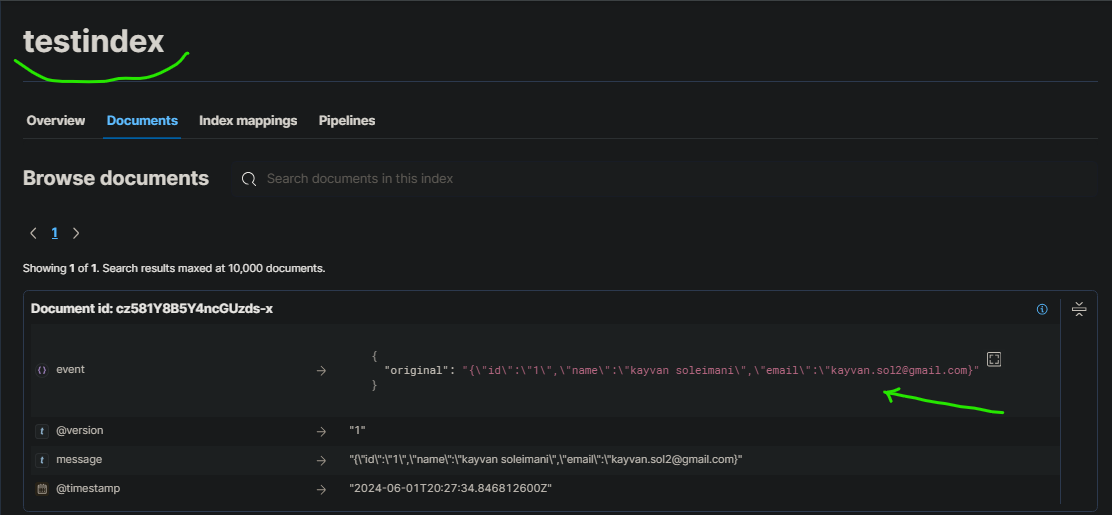
- After some seconds, data appear at your elastic index :
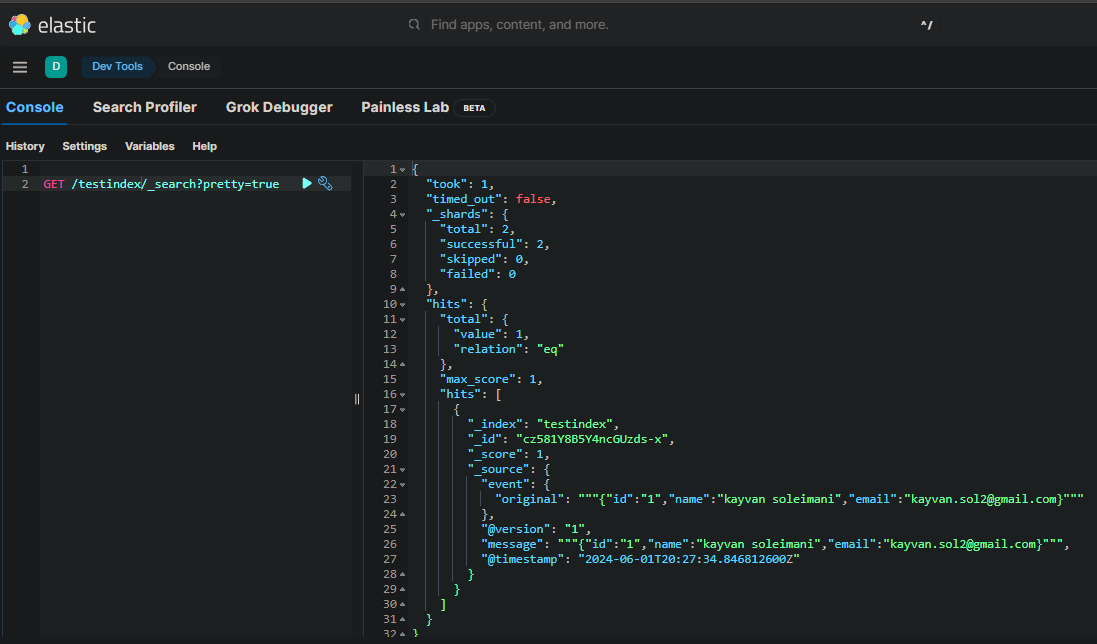
- You can search index records via Dev Tools at kibana :