-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7
MirrorSpecies
A mirror species is a species whose population is automatically managed with respect to another species. Whenever an agent is created or destroyed from the other species, an instance of the mirror species is created or destroyed. Each of these 'mirror agents' has access to its reference agent (called its target).
Mirror species can be used in different situations but the one we describe here is more oriented towards visualization purposes.
A mirror species can be defined using the mirrors facet as following:
species B mirrors: A { }
In this case, the species B mirrors the species A.
By default, the location of the species B will be random but in many cases, one wants to place the mirror agent at the same location as the reference species. This can be achieved by simply adding the following lines in the mirror species:
species B mirrors: A{
point location <- target.location update: target.location;
}
target is a built-in attribute of a mirror species. It refers to the instance of the species tracked.
In the same spirit, any attribute of a reference species can be reached using the same syntax. For instance, if the species A has an attribute called attribute1 of type int it is possible to get this attribute from the mirror species B using the following syntax:
int value <- target.attribute1;
To practice a bit with the mirror notion, we will now build a simple model displaying a species A (aspect: white circle) moving randomly, and another species B (aspect: blue sphere) with the species A location on x and y, with an upper value for the z-axis.
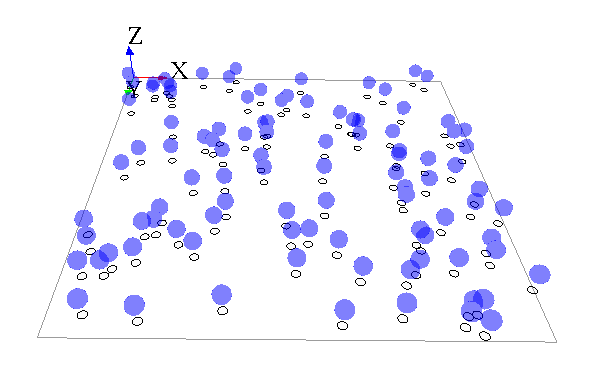
Here is an example of an implementation for this model:
model Mirror
global {
init{
create A number:100;
}
}
species A skills:[moving]{
reflex update{
do wander;
}
aspect base{
draw circle(1) color: #white border: #black;
}
}
species B mirrors: A{
point location <- target.location update: {target.location.x,target.location.y,target.location.z+5};
aspect base {
draw sphere(2) color: #blue;
}
}
experiment mirroExp type: gui {
output {
display superposedView type: opengl{
species A aspect: base;
species B aspect: base transparency:0.5;
}
}
}
- Installation and Launching
- Workspace, Projects and Models
- Editing Models
- Running Experiments
- Running Headless
- Preferences
- Troubleshooting
- Introduction
- Manipulate basic Species
- Global Species
- Defining Advanced Species
- Defining GUI Experiment
- Exploring Models
- Optimizing Models
- Multi-Paradigm Modeling
- Manipulate OSM Data
- Cleaning OSM Data
- Diffusion
- Using Database
- Using FIPA ACL
- Using BDI with BEN
- Using Driving Skill
- Manipulate dates
- Manipulate lights
- Using comodel
- Save and restore Simulations
- Using network
- Headless mode
- Using Headless
- Writing Unit Tests
- Ensure model's reproducibility
- Going further with extensions
- Built-in Species
- Built-in Skills
- Built-in Architecture
- Statements
- Data Type
- File Type
- Expressions
- Exhaustive list of GAMA Keywords
- Installing the GIT version
- Developing Extensions
- Introduction to GAMA Java API
- Using GAMA flags
- Creating a release of GAMA
- Documentation generation