generated from jhudsl/OTTR_Template
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
89 changed files
with
1,433 additions
and
1,999 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1 @@ | ||
| # Fundamentals Exercises |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,228 @@ | ||
| # Fundamentals | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ```{r, echo=F, message=F, warning=F} | ||
| library(tidyverse) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Goals of this course | ||
|
|
||
| - Continue building *programming fundamentals*: how to make use of complex data structures, use custom functions built by other R users, and creating your own functions. How to iterate repeated tasks that scales naturally. | ||
|
|
||
| - Continue exploration of *data science fundamentals*: how to clean messy data to a Tidy form for analysis. | ||
|
|
||
| - Outcome: Conduct a full analysis in the data science workflow (minus model). | ||
|
|
||
| 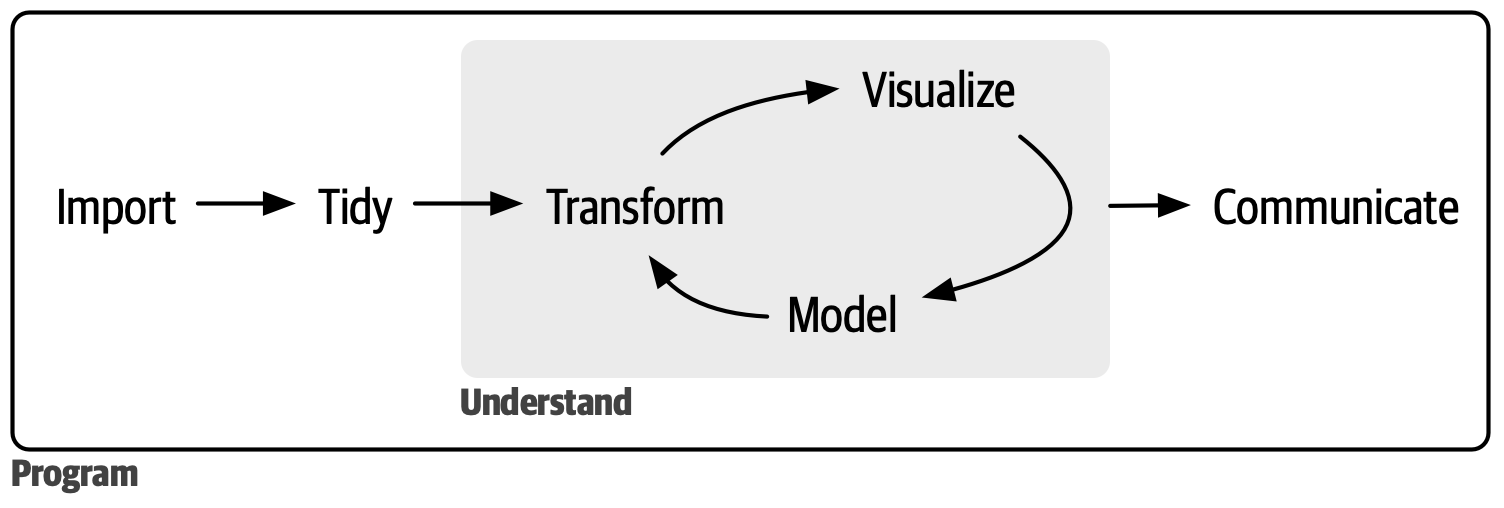{width="450"} | ||
|
|
||
| ## Data types in R | ||
|
|
||
| - Numeric: 18, -21, 65, 1.25 | ||
|
|
||
| - Character: "ATCG", "Whatever", "948-293-0000" | ||
|
|
||
| - Logical: TRUE, FALSE | ||
|
|
||
| - Missing values: `NA` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Data structures | ||
|
|
||
| - Vector | ||
|
|
||
| - **Factor** | ||
|
|
||
| - **List** | ||
|
|
||
| - Dataframe | ||
|
|
||
| ## Vector | ||
|
|
||
| We know what an **(atomic) vector** is: it can contains a data type, and all elements must be the same data type. | ||
|
|
||
| {width="400"} | ||
|
|
||
| - We can test whether a vector is a certain type with `is.___()` functions, such as `is.character()`. | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| is.character(c("hello", "there")) | ||
| ``` | ||
| For `NA`, the test will return a vector testing each element, because `NA` can be mixed into other values: | ||
| ```{r} | ||
| is.na(c(34, NA)) | ||
| ``` | ||
| - We can **coerce** vectors from one type to the other with `as.___()` functions, such as `as.numeric()` | ||
| ```{r} | ||
| as.numeric(c("23", "45")) | ||
| as.numeric(c(TRUE, FALSE)) | ||
| ``` | ||
| - It is common to have metadata **attributes,** such as **names,** attached to R data structures. | ||
| ```{r} | ||
| x = c(1, 2, 3) | ||
| names(x) = c("a", "b", "c") | ||
| x | ||
| ``` | ||
|  | ||
| We can look for more general attributes via the `attributes()` function: | ||
| ```{r} | ||
| attributes(x) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### Ways to subset a vector | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Positive numeric vector | ||
| 2. Negative numeric vector performs *exclusion* | ||
| 3. Logical vector | ||
|
|
||
| ### Practice implicit subsetting | ||
|
|
||
| 1. How do you subset the following vector so that it only has positive values? | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| data = c(2, 4, -1, -3, 2, -1, 10) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| data[data > 0] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 2. How do you subset the following vector so that it has doesn't have the character "temp"? | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| chars = c("temp", "object", "temp", "wish", "bumblebee", "temp") | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| chars[chars != "temp"] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 3. How do you subset the following vector so that it has no `NA` values? | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| vec_with_NA = c(2, 4, NA, NA, 3, NA) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| vec_with_NA[!is.na(vec_with_NA)] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Dataframes | ||
|
|
||
| Usually, we load in a dataframe from a spreadsheet or a package, but we can create a new dataframe by using vectors of the same length via the `data.frame()` function: | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| df = data.frame(x = 1:3, y = c("cup", "mug", "jar")) | ||
| attributes(df) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| library(palmerpenguins) | ||
| attributes(penguins) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Why are row names [undesirable](https://adv-r.hadley.nz/vectors-chap.html#rownames)? | ||
|
|
||
| Sometimes, data frames will be in a format called "tibble", as shown in the `penguins` class names as "tbl_df", and "tbl". | ||
|
|
||
| ### Subsetting dataframes | ||
|
|
||
| *Getting one single column:* | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| penguins$bill_length_mm | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| *I want to select columns `bill_length_mm`, `bill_depth_mm`, `species`, and filter for `species` that are "Gentoo":* | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| penguins_select = select(penguins, bill_length_mm, bill_depth_mm, species) | ||
| penguins_gentoo = filter(penguins_select, species == "Gentoo") | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| or | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| penguins_select_2 = penguins[, c("bill_length_mm", "bill_depth_mm", "species")] | ||
| penguins_gentoo_2 = penguins_select_2[penguins$species == "Gentoo" ,] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| or | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| penguins_gentoo_2 = penguins_select_2[penguins$species == "Gentoo", c("bill_length_mm", "bill_depth_mm", "species")] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| *I want to filter out rows that have `NA`s in the column `bill_length_mm`:* | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| penguins_clean = filter(penguins, !is.na(bill_length_mm)) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| or | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| penguins_clean = penguins[!is.na(penguins$bill_depth_mm) ,] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Lists | ||
|
|
||
| Lists operate similarly as vectors as they group data into one dimension, but each element of a list can be any data type *or data structure*! | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| l1 = list( | ||
| 1:3, | ||
| "a", | ||
| c(TRUE, FALSE, TRUE), | ||
| c(2.3, 5.9) | ||
| ) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| Unlike vectors, you access the elements of a list via the double bracket `[[]]`. You access a smaller list with single bracket `[]`. (More discussion on the different uses of the bracket [here](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1169456/the-difference-between-bracket-and-double-bracket-for-accessing-the-el).) | ||
|
|
||
| Here's a [nice metaphor](https://adv-r.hadley.nz/subsetting.html#subset-single): | ||
|
|
||
| > If list `x` is a train carrying objects, then `x[[5]]` is the object in car 5; `x[4:6]` is a train of cars 4-6. | ||
| ```{r} | ||
| l1[[1]] | ||
| l1[[1]][2] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Use `unlist()` to coerce a list into a vector. Notice all the automatic coersion that happened for the elements. | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| unlist(l1) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| We can give **names** to lists: | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| l1 = list( | ||
| ranking = 1:3, | ||
| name = "a", | ||
| success = c(TRUE, FALSE, TRUE), | ||
| score = c(2.3, 5.9) | ||
| ) | ||
| #or | ||
| names(l1) = c("ranking", "name", "success", "score") | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| And access named elements of lists via the `$` operation: | ||
|
|
||
| ```{r} | ||
| l1$score | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Therefore, `l1$score` is the same as `l1[[4]]` and is the same as `l1[["score"]]`. | ||
|
|
||
| A dataframe is just a named list of vectors of same length with **attributes** of (column) `names` and `row.names`. |
This file was deleted.
Oops, something went wrong.
Oops, something went wrong.