Is a fork of amdgpu-fan, with security updates and added functionality. This is intended for stand-alone GPU's and not integrated APU's.
- alternatives abandoned
- lacking required features
- security fixes not addressed
- basic functionality not working
As of a couple years ago, and is no longer applying any security fixes to their project or improvements. There were also some bugs that bothered me with the project when I tried to get it up and running. Features missing
There are a number of features that I wanted, but were not available.
- Thresholds allow temperature range before changing fan speed
- Frequency setting to allow better control
- Monitoring to be able to see real-time fan speeds and temperature
There are some un-addressed pull requests for some recent YAML vulnerabilities that are still present in the old amdgpu_fan project, that I’ve addressed in this fork.
Setting the card to system managed using the amdgpu_fan pegs your GPU fan at 100%, instead of allowing the system to manage the fan settings. I fixed that bug as well in this release.
These are all addressed in Amdfan, and as long as I’ve still got some AMD cards I intend to at least maintain this for myself. And anyone’s able to help out since this is open source. I would have liked to just contribute these fixes to the main project, but it’s now inactive.
Usage: amdfan.py [OPTIONS]
Options:
--daemon Run as daemon applying the fan curve
--monitor Run as a monitor showing temp and fan speed
--manual Manually set the fan speed value of a card
--configuration Prints out the default configuration for you to use
--service Prints out the amdfan.service file to use with systemd
--help Show this message and exit.Amdfan is also runnable as a systemd service, with the provided amdfan.service.
You can use Amdfan to monitor your AMD video cards using the --monitor flag.
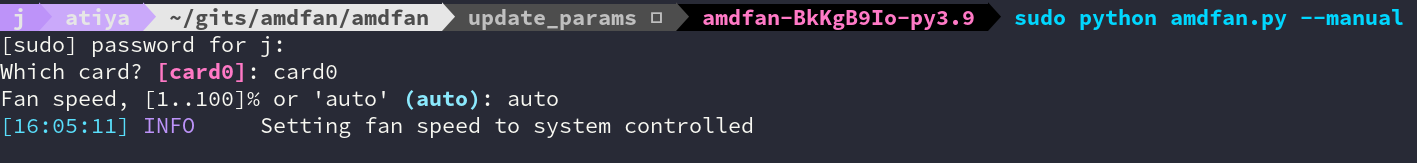
Alternatively if you don't want to set a fan curve, you can just apply a fan setting manually.
Also allows you to revert the fan control to the systems default behavior by using the "auto" parameter.
This will dump out the default configuration that would get generated for /etc/amdfan.yml when you first run it as a service. This allows you to configure the settings prior to running it as a daemon if you wish.
Running amdfan --configuration will output the following block to STDOUT.
#Fan Control Matrix.
# [<Temp in C>,<Fanspeed in %>]
speed_matrix:
- [4, 4]
- [30, 33]
- [45, 50]
- [60, 66]
- [65, 69]
- [70, 75]
- [75, 89]
- [80, 100]
# Current Min supported value is 4 due to driver bug
#
# Optional configuration options
#
# Allows for some leeway +/- temp, as to not constantly change fan speed
# threshold: 4
#
# Frequency will change how often we probe for the temp
# frequency: 5
#
# While frequency and threshold are optional, I highly recommend finding
# settings that work for you. I've included the defaults I use above.
#
# cards:
# can be any card returned from `ls /sys/class/drm | grep "^card[[:digit:]]$"`
# - card0You can use this to generate your configuration by doing amdfan --configuration > amdfan.yml, you can then modify the settings and place it in /etc/amdfan.yml for when you would like to run it as a service.
This is just a convenience method for dumping out the amdfan.service that would get installed if you used a package manager to install amdfan. Useful if you installed the module via pip, pipenv or poetry.
Running amdfan --service will output the following block to STDOUT.
[Unit]
Description=amdfan controller
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/amdfan --daemon
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetMonitoring fan speeds and temperatures can run with regular user permissions.
root permissions are required for changing the settings / running as a daemon.
Below is the settings that I use on my machines to control the fan curve without too much fuss, but you should find a frequency and threshold setting that works for your workloads.
/etc/amdfan.yml
speed_matrix:
- [4, 4]
- [30, 33]
- [45, 50]
- [60, 66]
- [65, 69]
- [70, 75]
- [75, 89]
- [80, 100]
threshold: 4
frequency: 5If you installed via the AUR, the service is already installed, and you just need to start/enable it. If you installed via pip/pipenv or poetry, you can generate your systemd service file with the following command.
amdfan --service > amdfan.service && sudo mv amdfan.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/To run the service, you can run the following commands to start/enable the service.
sudo systemctl start amdfan
sudo systemctl enable amdfanAfter you've started it, you may want to edit the settings found in /etc/amdfan.yml. Once your happy with those, you can restart amdfan with the following command.
sudo systemctl restart amdfanYou can check the systemd service status with the following command:
systemctl status amdfanBuilding the Arch package assumes you already have a chroot env setup to build packages.
git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/amdfan.git
cd amdfan/
makechrootpkg -c -r $HOME/$CHROOTsudo pacman -U --asdeps amdfan-*-any.pkg.tar.zstYou can also install amdfan from pypi using something like poetry.
poetry init
poetry add amdfan
poetry run amdfan --helpRequires poetry to be installed
git clone [email protected]:mcgillij/amdfan.git
cd amdfan/
poetry build
