-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Conditional and Boolean Operators
This section explains operators with which you conditionally emit or transform Observables, or can do boolean evaluations of them:
-
amb( )— given two or more source Observables, emits all of the items from the first of these Observables to emit an item -
defaultIfEmpty( )— emit items from the source Observable, or emit a default item if the source Observable completes after emitting no items -
doWhile( )— emit the source Observable's sequence, and then repeat the sequence as long as a condition remains true -
ifThen( )— only emit the source Observable's sequence if a condition is true, otherwise emit an empty or default sequence -
skipUntil( )— discard items emitted by a source Observable until a second Observable emits an item, then emit the remainder of the source Observable's items -
skipWhile( )andskipWhileWithIndex( )— discard items emitted by an Observable until a specified condition is false, then emit the remainder -
switchCase( )— emit the sequence from a particular Observable based on the results of an evaluation -
takeUntil( )— emits the items from the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item -
takeWhile( )andtakeWhileWithIndex( )— emit items emitted by an Observable as long as a specified condition is true, then skip the remainder -
whileDo( )— if a condition is true, emit the source Observable's sequence and then repeat the sequence as long as the condition remains true
-
all( )— determine whether all items emitted by an Observable meet some criteria -
contains( )— determine whether an Observable emits a particular item or not -
exists( )andisEmpty( )— determine whether an Observable emits any items or not -
sequenceEqual( )— test the equality of the sequences emitted by two Observables
given two or more source Observables, emits all of the items from the first of these Observables to emit an item

When you pass a number of source Observables to amb( ), it will pass through the emissions and messages of exactly one of these Observables: the first one that emits an item to amb( ). It will ignore and discard the emissions of all of the other source Observables.
emit items from the source Observable, or emit a default item if the source Observable completes after emitting no items

- javadoc:
defaultIfEmpty(default) - RxJS:
defaultIfEmpty - Linq:
DefaultIfEmpty - Introduction to Rx: DefaultIfEmpty
emit the source Observable's sequence, and then repeat the sequence as long as a condition remains true
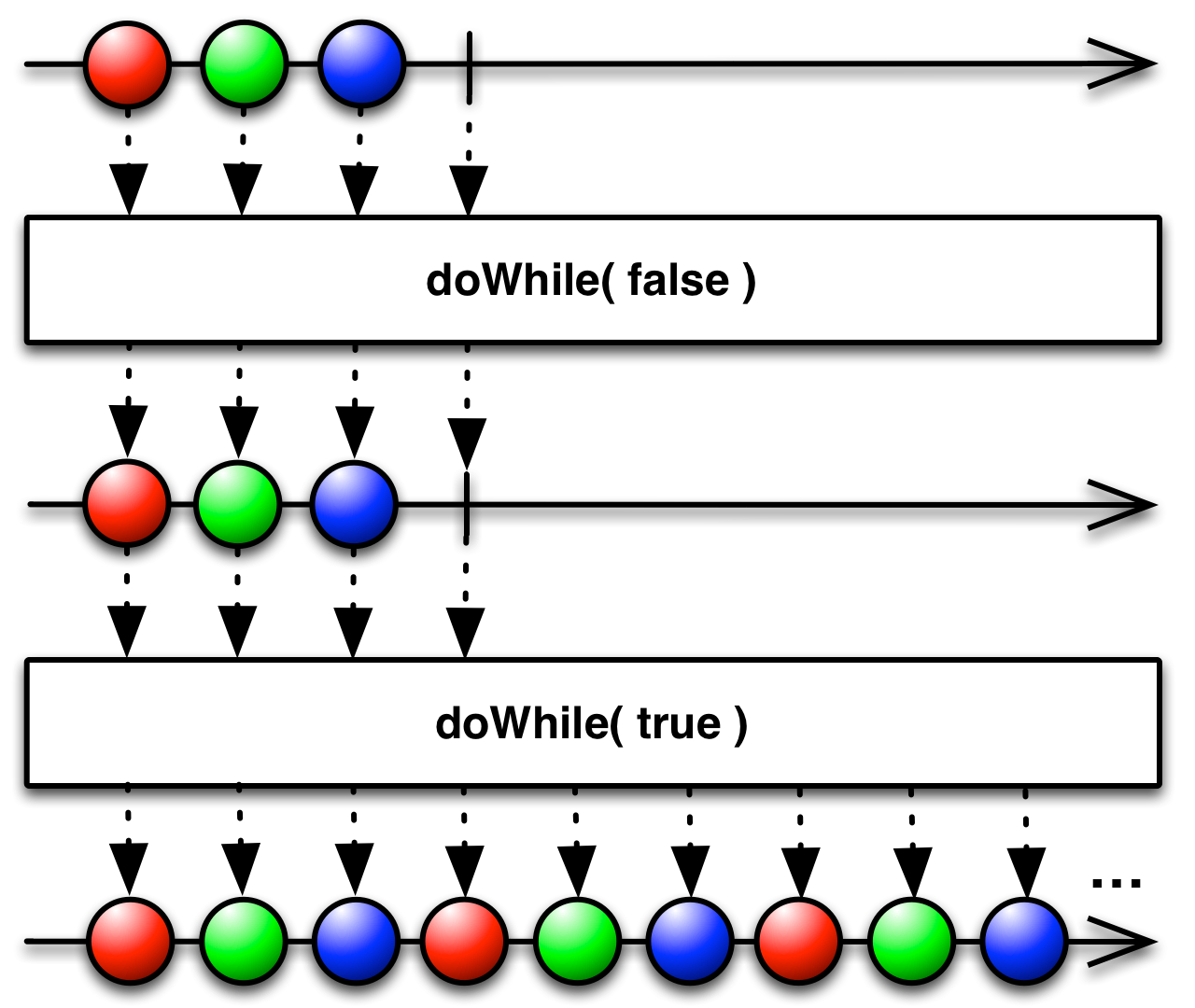
The doWhile( ) operator emits the sequence emitted by the source Observable and then checks to see if a specified condition is true; if so it will resubscribe and reemit the source Observable's sequence, repeating this process until the condition becomes false.
- RxJS:
doWhile
only emit the source Observable's sequence if a condition is true, otherwise emit an empty or default sequence
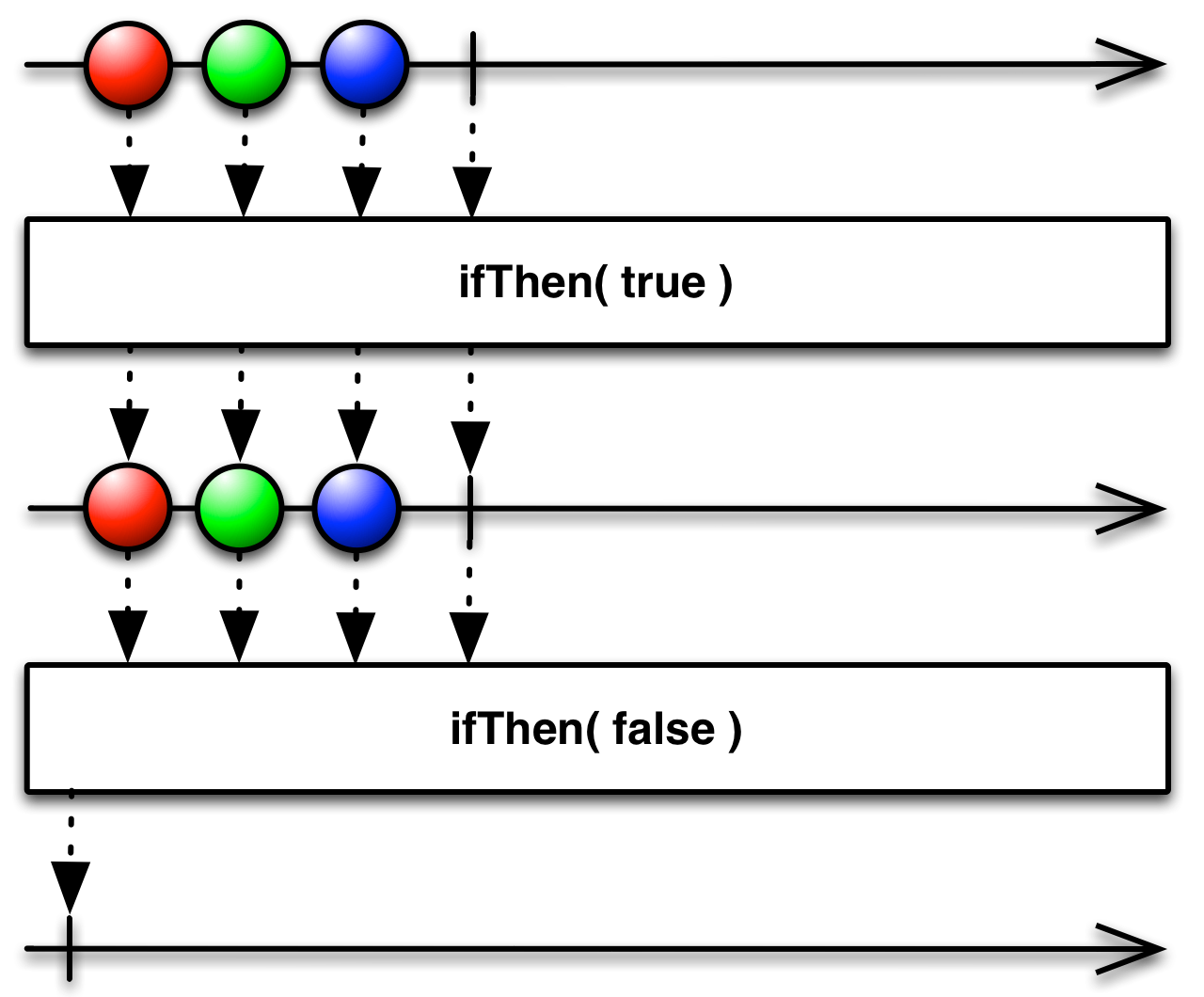
The ifThen( ) operator evaluates a function and emits the source Observable's sequence if the function evaluates as true, and otherwise either emits an empty sequence or the sequence from an alternate Observable you specify.
discard items emitted by a source Observable until a second Observable emits an item, then emit the remainder of the source Observable's items

- javadoc:
skipUntil(other) - RxJS:
skipUntil - Linq:
SkipUntil - Introduction to Rx: SkipUntil and TakeUntil
discard items emitted by an Observable until a specified condition is false, then emit the remainder

The skipWhile( ) method returns an Observable that discards items emitted by the source Observable until such time as a function applied to an item emitted by that Observable returns false, whereupon the new Observable emits that item and the remainder of the items emitted by the source Observable.
numbers = Observable.from( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] );
numbers.skipWhile({ (5 != it) }).subscribe(
{ println(it); }, // onNext
{ println("Error: " + it.getMessage()); }, // onError
{ println("Sequence complete"); } // onCompleted
);5
6
7
8
9
Sequence complete
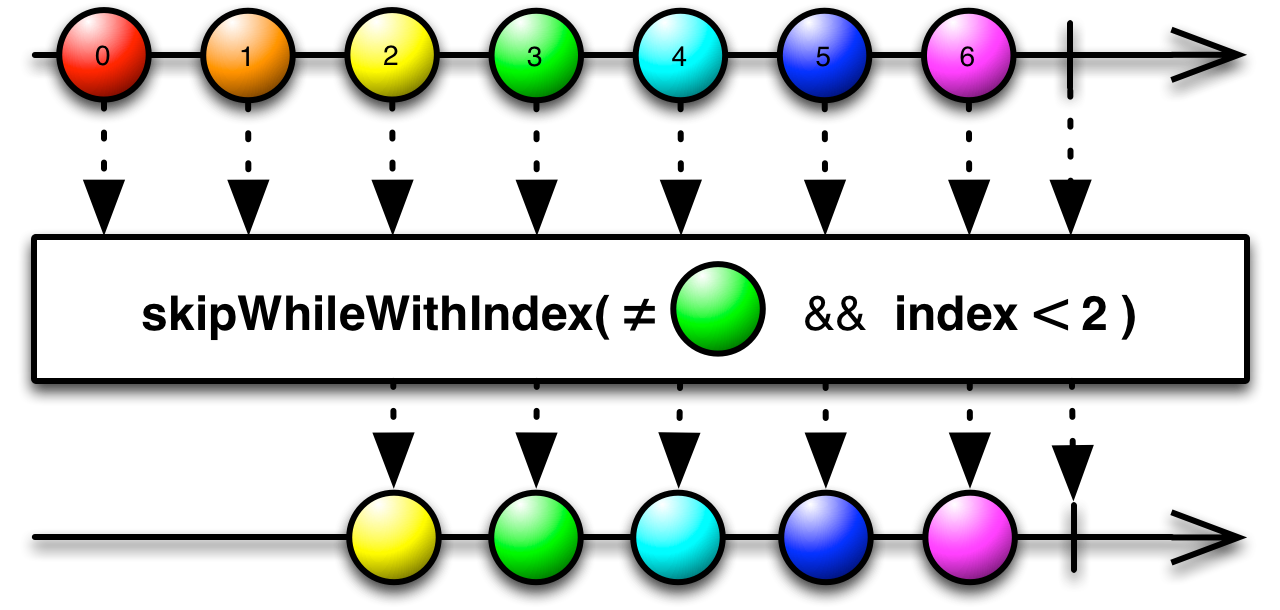
The skipWhileWithIndex( ) method is similar, but your function takes an additional parameter: the (zero-based) index of the item being emitted by the source Observable.
numbers = Observable.from( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] );
numbers.skipWhileWithIndex({ it, index -> ((it < 6) || (index < 5)) }).subscribe(
{ println(it); }, // onNext
{ println("Error: " + it.getMessage()); }, // onError
{ println("Sequence complete"); } // onCompleted
);6
7
8
9
Sequence complete
- javadoc:
skipWhile(predicate) - javadoc:
skipWhileWithIndex(predicate) - Linq:
SkipWhile - RxJS:
skipWhile - Introduction to Rx: SkipWhile and TakeWhile

The switchCase( ) operator evaluates a case and passes control to a particular one of a set of Observables based on the case.
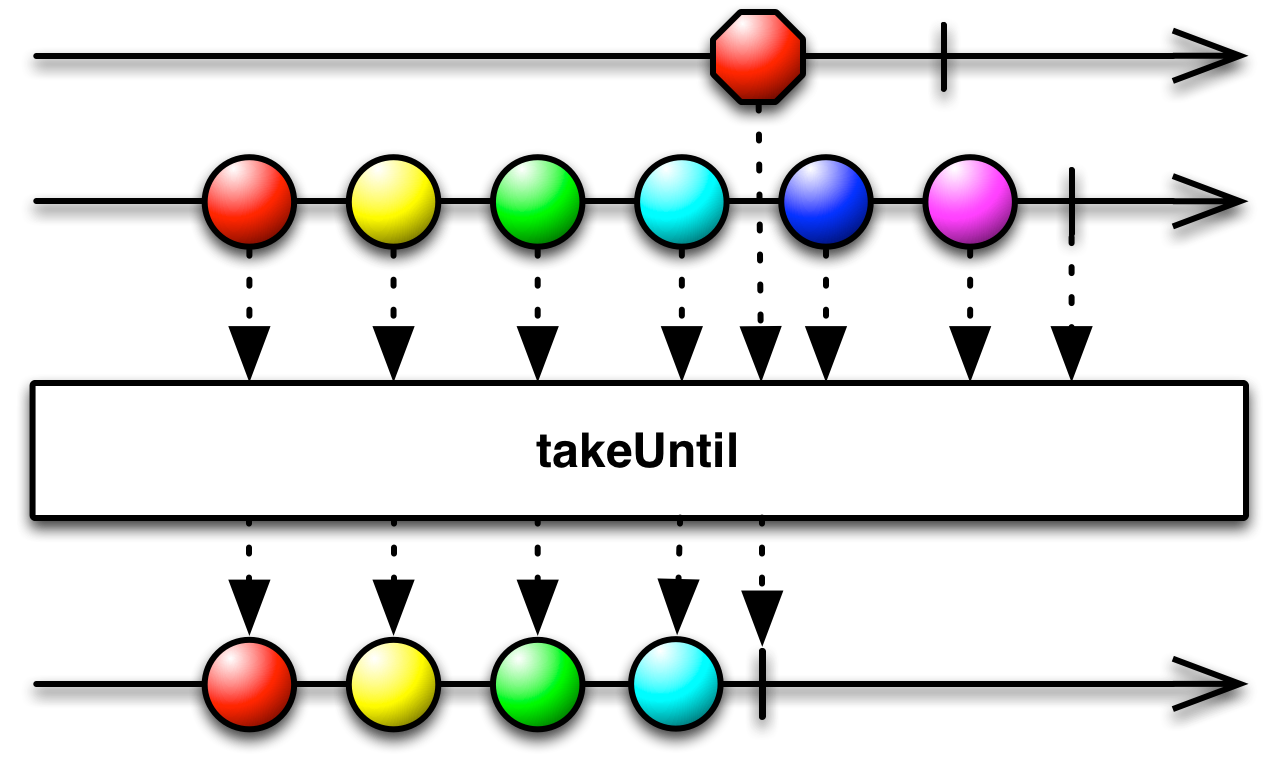
- javadoc:
takeUntil(other) - RxJS:
takeUntil - Linq:
TakeUntil
emit items emitted by an Observable as long as a specified condition is true, then skip the remainder

The takeWhile( ) method returns an Observable that mirrors the behavior of the source Observable until such time as a function applied to an item emitted by that Observable returns false, whereupon the new Observable invokes onCompleted( ).
numbers = Observable.from( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] );
numbers.takeWhile({ ((it < 6) || (0 == (it % 2))) }).subscribe(
{ println(it); }, // onNext
{ println("Error: " + it.getMessage()); }, // onError
{ println("Sequence complete"); } // onCompleted
);1
2
3
4
5
6
Sequence complete
 The
The takeWhileWithIndex( ) method is similar, but your function takes an additional parameter: the (zero-based) index of the item being emitted by the source Observable.
numbers = Observable.from( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] );
numbers.takeWhileWithIndex({ it, index -> ((it < 6) || (index < 5)) }).subscribe(
{ println(it); }, // onNext
{ println("Error: " + it.getMessage()); }, // onError
{ println("Sequence complete"); } // onCompleted
);1
2
3
4
5
Sequence complete
- javadoc:
takeWhile(predicate) - javadoc:
takeWhileWithIndex(predicate) - Linq:
TakeWhile - RxJS:
takeWhile - Introduction to Rx: SkipWhile and TakeWhile
if a condition is true, emit the source Observable's sequence and then repeat the sequence as long as the condition remains true
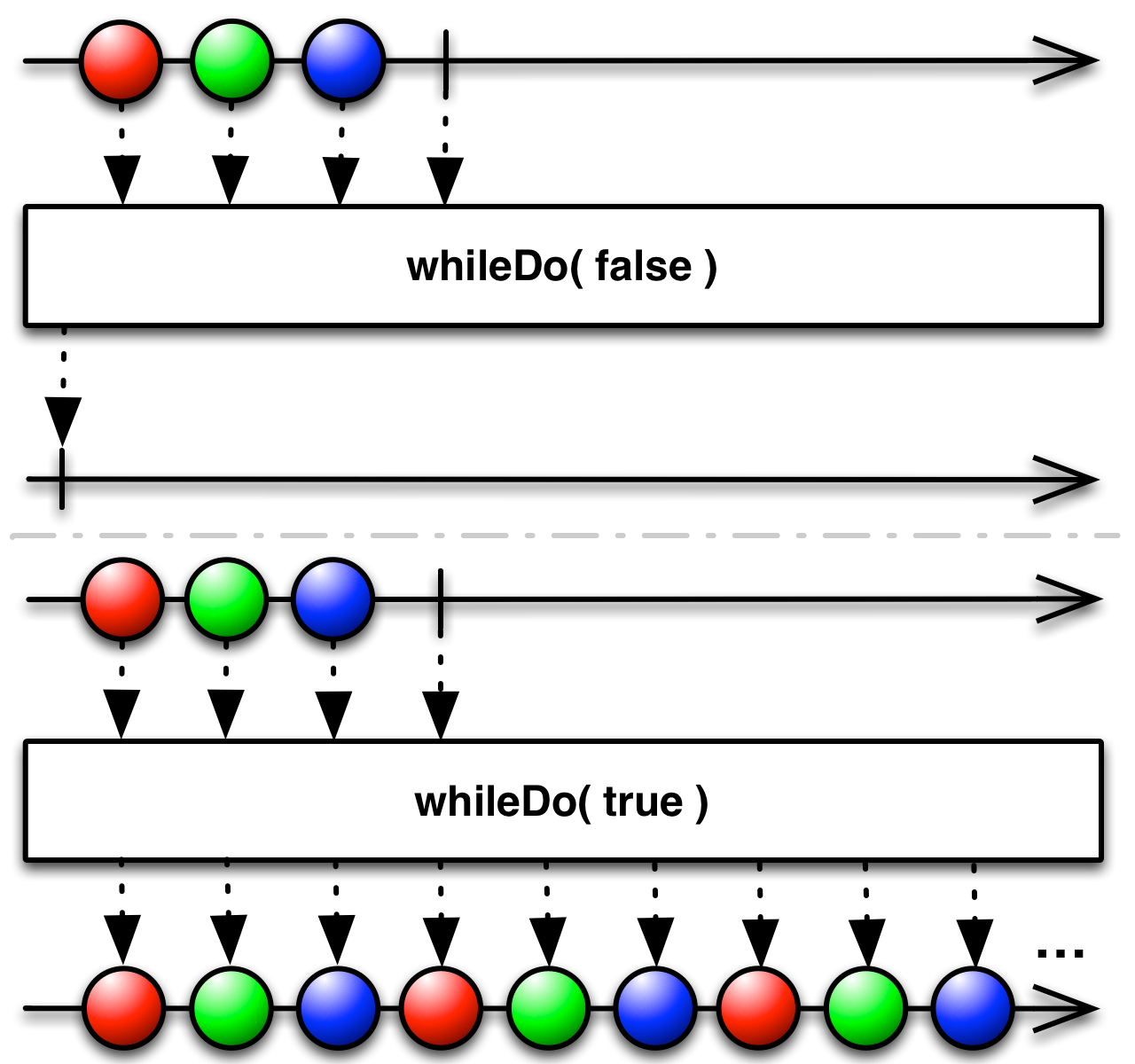
If a specified condition evaluates as true, whileDo( ) will emit the sequence emitted by the source Observable. It will then check to see if the condition remains true and will resubscribe and reemit the source Observable's sequence if so; repeating this process until the condition becomes false.
- RxJS:
while

Pass an function to all( ) that accepts an item emitted by the source Observable and returns a boolean value based on an evaluation of that item, and all( ) will emit true if and only if that function returned true for every item emitted by the source Observable.
numbers = Observable.from([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
println("all even?" )
numbers.all({ 0 == (it % 2) }).subscribe({ println(it); });
println("all positive?");
numbers.all({ 0 < it }).subscribe({ println(it); });all even?
false
all positive?
true
- javadoc:
all(predicate) - RxJS:
all - Linq:
All - Introduction to Rx: All
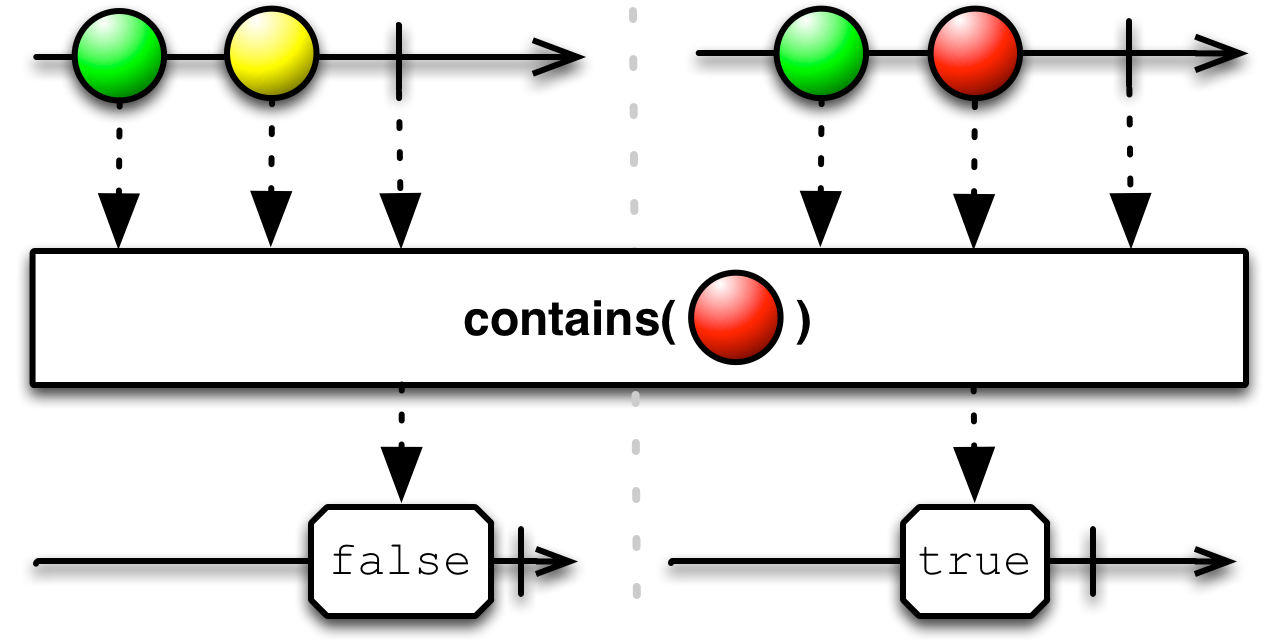
Pass the contains( ) operator a particular item, and it will emit true if that item is emitted by the source Observable, or false if the source Observable terminates without emitting that item.
- javadoc:
contains(item) - Linq:
Contains - RxJS:
contains - Introduction to Rx: Contains
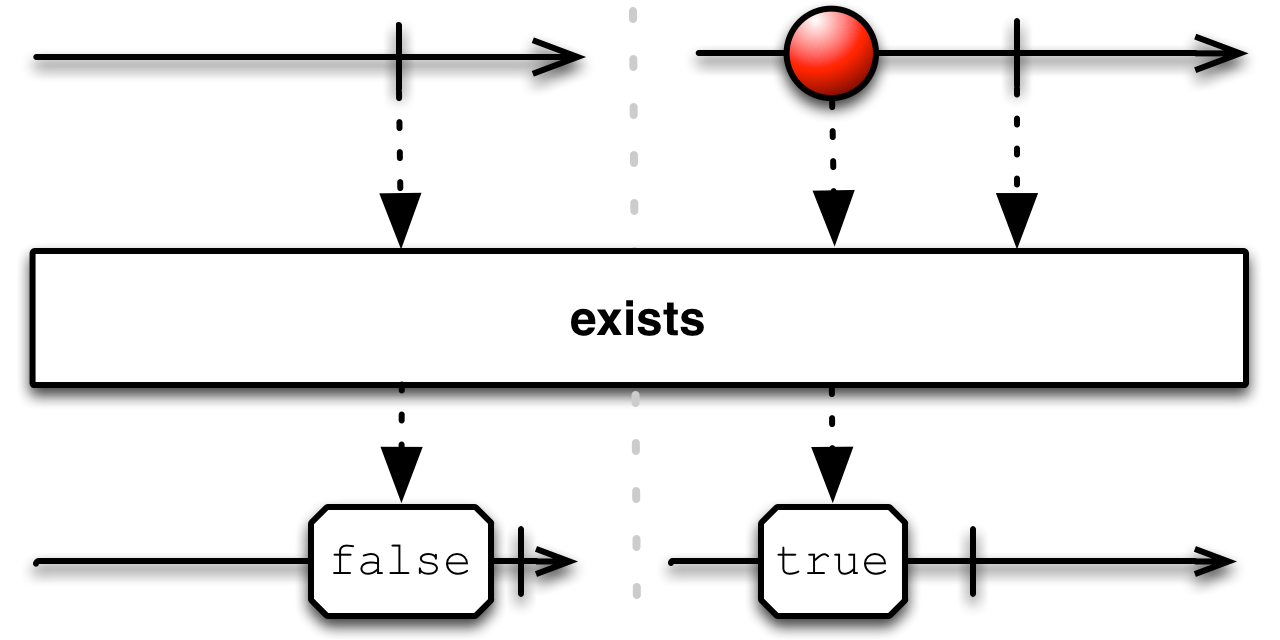
When you apply the exists( ) operator to a source Observable, the resulting Observable will emit true and complete if the source Observable emits one or more items before completing, or it will emit false and complete if the source Observable completes without emitting any items.
 The inverse of this is the
The inverse of this is the isEmpty( ) operator. Apply it to a source Observable and the resulting Observable will emit true and complete if the source Observable completes without emitting any items, or it will emit false and complete if the source Observable emits any item before completing.
- javadoc:
exists(predicate) - javadoc:
isEmpty() - RxJS:
anyandisEmpty - Linq:
Any - Introduction to Rx: Any
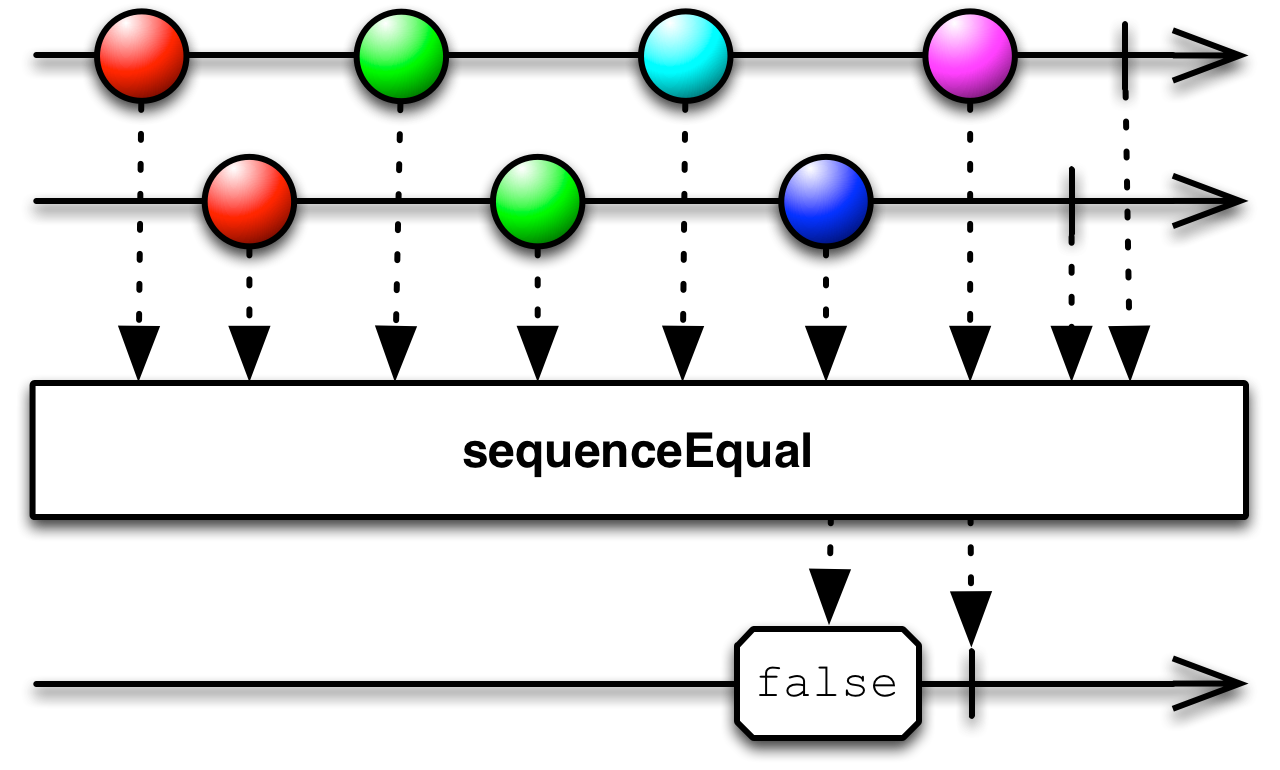
Pass sequenceEqual( ) two Observables, and it will compare the items emitted by each Observable, and emit true only if both sequences are the same. You can optionally pass a third parameter: a function that accepts two items and returns true if they are equal according to a standard of your choosing.
def firstfour = Observable.from([1, 2, 3, 4]);
def firstfouragain = Observable.from([1, 2, 3, 4]);
def firstfive = Observable.from([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
def firstfourscrambled = Observable.from([3, 2, 1, 4]);
println('firstfour == firstfive?');
Observable.sequenceEqual(firstfour, firstfive).subscribe({ println(it); });
println('firstfour == firstfouragain?');
Observable.sequenceEqual(firstfour, firstfouragain).subscribe({ println(it); });
println('firstfour == firstfourscrambled?');
Observable.sequenceEqual(firstfour, firstfourscrambled).subscribe({ println(it); });firstfour == firstfive?
false
firstfour == firstfouragain?
true
firstfour == firstfourscrambled?
false
A Netflix Original Production
Tech Blog | Twitter @NetflixOSS | Twitter @RxJava | Jobs