formjs is a wrapper around axios and a form helper, highly inspired from InertiaJS for both vue 2 & 3. It's a tool to use to handle form and API calls when building client-side application.
yarn add formjs-vue2It works for both vue 2 & 3
It is possible to perform API call using formjs with the help of http.visit() method.
<script setup>
import { http } from "formjs-vue2"
http.visit(url,{
method: 'get',
data: {},
headers: {},
forceFormData: false,
onSuccess:(response)=>{},
onErrors: (errors) => {},
onError: (error) => {},
onFinish: () => {},
instance: axios(),
})
</script>However, it's usually easier to use one of formjs's quick shortcut methods. These methods have all the same options as http.visit().
<script setup>
import { http } from "formjs-vue2"
http.get(url, data, options)
http.post(url, data, options)
http.put(url, data, options)
http.delete(url, options)
</script>Uploading files via put is not supported in Laravel. Instead, make the request via post, including a _method field set to put. This is called form method spoofing.
You may use the data option to add data to the request.
<script setup>
import { http } from "formjs-vue2"
http.visit('/users', {
method: 'post',
data: {
name: 'John Doe',
email: '[email protected]',
},
})
</script>For convenience, the get(), post() and put() methods all accept data as their second argument.
<script setup>
import { http } from "formjs-vue2"
http.post('/users', {
data: {
name: 'John Doe',
email: '[email protected]',
},
})
</script>formjs provides four different callbacks onSuccess, onErrors, onError and onFinish to handle the API responses.
It is called when response status is in 200 (success) range. It gets response as callback argument.
<script setup>
import { http } from "formjs-vue2"
http.get('/users',data, {
onSuccess: (response)=>{
console.log('I am success')
}
})
</script>formjs provides dedicated callback to handle validation errors. Any API response return with 422 status will be captured by onErrors callback. The validation errors response should be in Laravel's error response format
<script setup>
import { http } from "formjs-vue2"
http.get('/users',data, {
onErrors: (errors)=>{
console.log(errors)
}
})
</script>It is called when the server return response of 400 to 500 status range.
<script setup>
import { http } from "formjs-vue2"
http.get('/users',data, {
onError: (error)=>{
console.log('something went wrong.')
}
})
</script>It is called everytime when the API call is completed, no matter what the response is. This callback can be used to track the loading state of a API call.
<script setup>
import { http } from "formjs-vue2"
import {ref} from "vue"
const isLoading = ref(false);
const getUsers = ()=>{
isLoading.value = true;
http.get('/users',data, {
onFinish: ()=>{
isLoading.value= false
}
})
}
</script>The headers option allows you to add custom headers to a request.
<script setup>
import { http } from "formjs-vue2"
http.post('/users', data, {
headers: {
'Custom-Header': 'value',
},
})
</script>The primary use case of formjs is to ease the form handling by reducing amount of boilerplate code needed for form submissions.
<template>
<div>
<input type="email" v-model="form.email">
<span v-if="form.errors.email" v-text="form.errors.email"/>
<button type="submit" :disabled="form.processing" @click="submit">Submit</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useForm } from "formjs-vue2"
const form = useForm({
email: "",
})
</script>To submit the form, you may use get, post, put, and delete methods.
form.submit(method, url, options)
form.get(url, options)
form.post(url, options)
form.put(url, options)
form.patch(url, options)
form.delete(url, options)The submit method supports all the above visit options, such as headers, forceFormData and all the event
callback, which can be helpful for performing the tasks based on the response of submission. For example, you might use the onSuccess callback to reset inputs to their original state.
form.post("/users", {
onSuccess: () => form.reset(),
})useForm composable also provides the onErrors callback for 422 status response. The callback shares the same signatures as above define for http.visit().
Besides that you generally don't require to implement this method manually, as useForm automatically maps the errors
into form. You may access the errors for a field with form.errors.{field}. For example, error for an input email can access with form.errors.email. However, the validation errors response
should be in Laravel's error response format
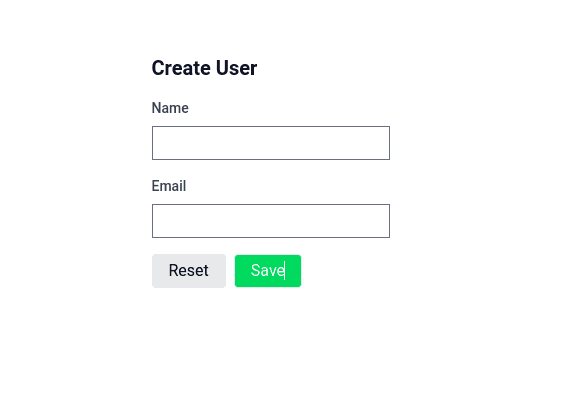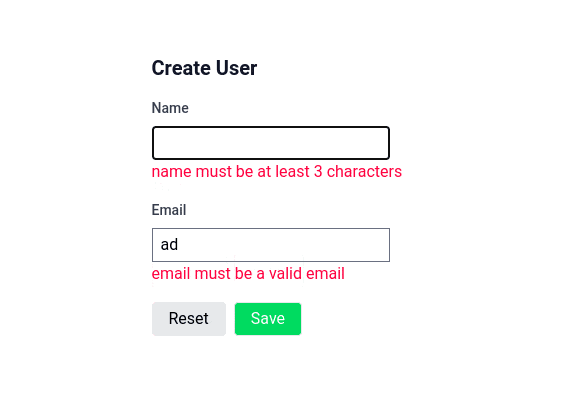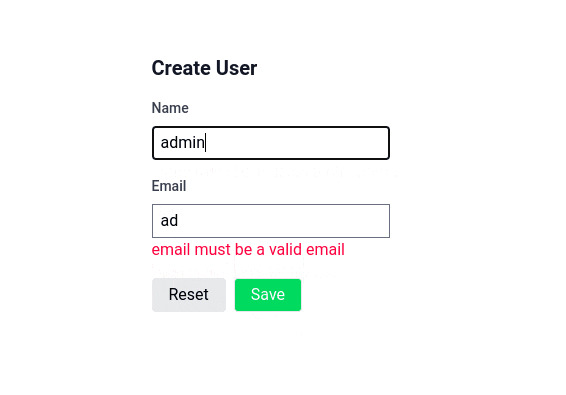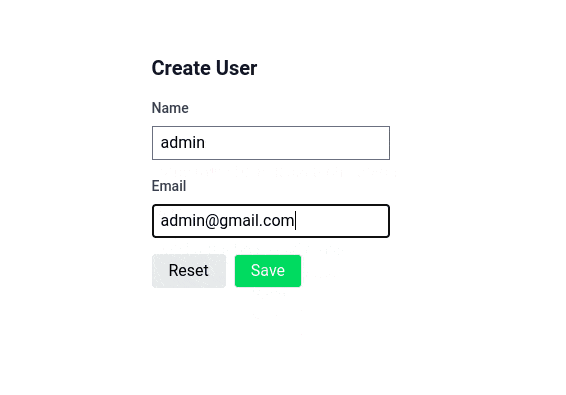
formjs can be used with yup to validate data in frontend side.
<template>
<div>
<input type="email" v-model="form.email" @blur="form.validate('email')">
<span v-if="form.errors.email" v-text="form.errors.email"/>
<button type="submit" :disabled="form.processing" @click="submit">Submit</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useForm } from "formjs-vue2"
import { object, string } from "yup"
const userStoreSchema = object({
email: string().email(),
firstname: string().min(8),
})
const form = useForm({
email: "",
firstname: "",
}, {schema: userStoreSchema})
const submit = async ()=>{
// validate all methods
await form.validate()
if(!form.hasErrors){
form.post('/some-endpoints')
}
}
</script>
// Somewhere in template
<input v-model="form.email" @input="form.validate('email')"/>Sometimes it is required to configure custom request.
import {useForm} from "formjs-vue2"
import {default as Axios} from "axios";
const instance = Axios.create({
baseURL: "https://custom-config.com",
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer token`,
},
})
const form = useForm({
email: null,
name: null,
}, { instance: instance })import {http} from "formjs-vue2"
http.post("api/users", {} , {
instance: instance,
})The FormJs package is open-sourced software licensed under the MIT license.