Manage Android app deployments to shared devices with ease
On all systems, a recent version of Git and Android Platform Tools are required.
Additionally, on all systems, adb and git must be on $PATH
(try typing adb in a terminal to check, or the script will let you know)
On Linux systems, grep, sed, mktemp, and ncurses' tput are required.
The script runs in bash.
To install on your system, copy the relevant script file to a directory on your $PATH.
On Linux, try ~/.local/bin, /usr/local/bin, or adjust your shell's startup script to put it in some other location.
On Windows, you could put it in C:\Windows, but it's easier to use the builtin "Edit the system environment variables" app to add a custom directory to your $PATH.
Without arguments, gitftc will display if a device is connected, and
its current state of the repository you are currently in.
To perform a manual deployment, run gitftc deploy (or gitftc d for short). This will
"deploy" the current Git commit and your staged changes to the connected device, making
them available for anyone else connected to the device in the future.
You can setup automatic deployments through Android Studio to run whenever you press the 'Run' button.
On Windows, you can use the excellent PowerShell plugin to add a configuration:
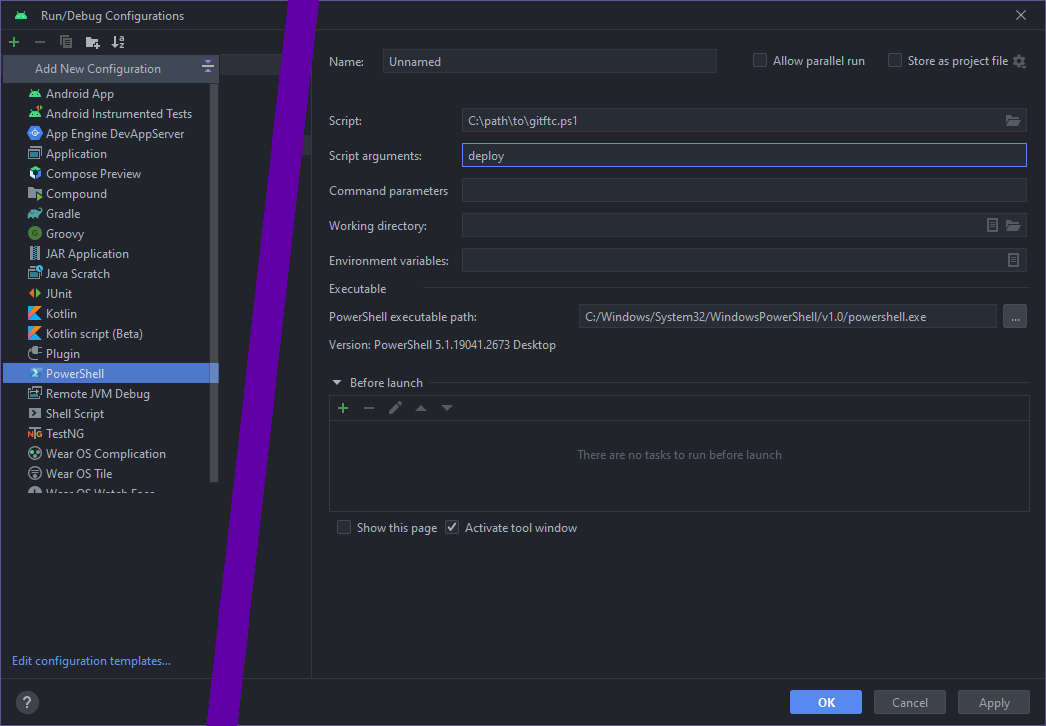
On Linux, you can use the builtin Shell Script configuration:
note: remember to set the Script Options to 'deploy', which I forgot to do in the screenshot, oops
Finally, go to your main build script (the one that runs the app) and add your other configuration as a Before launch task. This will run the script before each run of your app.
You can get your code back from the deployed device, provided you have the
deployed commit in your history. Run gitftc checkout (or gitftc c) to
checkout the appropriate commit and apply the staged changes patch.
To delete the deployment information from the device, run gitftc delete.


