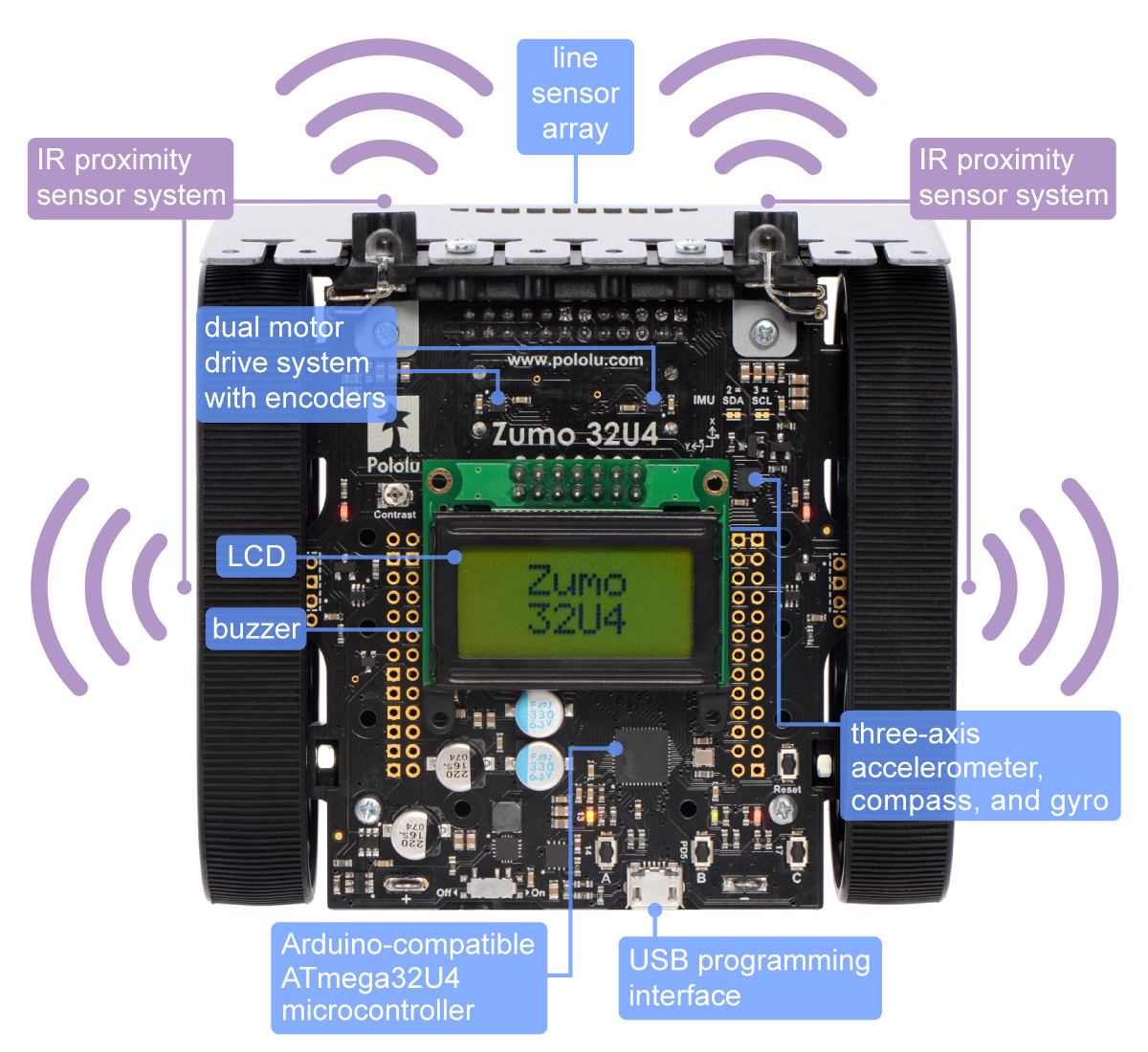
-
The goal of this project is to
- Allow two ZUMO32U4 robots to play a mini sumo match
- Have the robots know who won
- Enable the robots to wirelessly communicate match data to a master laptop
- Allow the robots to charge themselves wirelessly
- Allow the robots to reset for a new match automatically
- Create a machine learning exercise whereby the robots can learn the best strategy by playing each other
- Provide Brandeis students with an introduction to programming
-
Getting started
- Link to install all software
- And see example files in examples folder
-
Background information
-
Hardware + Current robot used
-
This project was conceived of by technical advisor Tim Hebert and is currently being implemented by the Brandeis Robotics Club
-
We are always looking for anyone who wants to contribute, email us!
Here is an example of a sumo match that is possible with this project, the example here is Zumo_Match_Distance:
- These libraries provide added functionality to Pololu's Zumo Shield Library
- They take a sensor or motor and make it more user friendly and add calibration
- includes calibration function
initializeCompass(), which makes sure accelerometer at rest reads no acceleration on x and y axes - The getter functions allow the robot's acceleration to be returned in centimeters per second squared
accel.getX() - The class can also return whether it has been collided with from rest
collided()See Was_Bumped - The class can print its acceleration to the serial monitor
printAccels()See Print_Accelerations
- Includes functions like DriveForward, DriveBackward, etc whic hlet the robot drive around.
- The simplest version
driveForward(500)would tell the robot to drive forward, wait half a second, and stop See Example - The more advanced version with no time parameter
driveForward()just sets the robot to drive forward and gives more user control.
- The simplest version
- The get and setPower method allow the robot to change its speed, so it can speed up or slow down wihtout hardcoding speed, like this
setPower(getPower()/2)which halves the robot's power. See Random Power
- Includes functions to play a song and individual notes with the buzzer
- See Example , which uses
play()to play a song andplay (NOTE_E(4))to play an individual note
- See Example , which uses
- These libraries build on the more low level programs to allow the robots to play a zumo match
- includes function to prompt a user to move the robot over the regions to be detected
calibrateLineSensors()See calibrate - to get the result, use
getThresholds()which returns a list of the numerical boundaries between regions - to get the list of regions (which could be in different order than you gave) use
getRegions()
- To use, you need the
setElements(String* regions, int numRegions, String regionsSeen[],bool USB) - To see what region the robot is over, use
getRegion()See Calibrate - To display individual sensor values, use
displayLineReadings()
- They are used to return whether the robot is on a line of tape and to print line sensor readings to the robot's display
- The boolean methods of the class are isInRing, isOnEdge, isOutBounds
- The getRegion method returns where the robot is in the ring
- The printAllSensors method displays the 3 used line sensor values on the robot's lcd
- An example file is provided
- It uses this library and the Drive library to keep the robot in a ring of tape
- The complex navigation program uses an extra line of tape on the outside of the ring to allow the robot to know when it lost a match
- This Library sorts a given array, which is useful in calibrating the line sensors
- An example file is provided
- It sorts 3 example arrays in a similar format to how theyd be used in a line sensor application
- This library is a wrapper class for the Arduino time function
- This library allows for the instantiation of a timer object which can return the current time, be reset, and be used on an interval
- This allows an arduino board to continually perform an update procedure without the use of delay statements
- The provided example file shows the suggested use of this class on a ZUMO32U4 robot using the [Arduino Integrated Development Enviornment](
- These example files aren't based on any one class but still represent useful endeavors of the robotics club
- As an introduction, the students started out with sample zumo behaviors See RoboticsClub_First_Meeting
- Over a few weeks, students worked on this program to allow the robot to determine its speedSee Calibrate
Wireless, programs written to allow the robot to drive wirelessly (provided code except remote control)
- Provideed Program allows robot to message eachother NRF24 Wireless_HowToMechatronicsRecieve and Wireless_HowToMexhantroincsTransmit
- Provided Program allows robot to cmmunicate with eachother over bluetooth Wireless_wifittest3w
- This Program allows the robot to be controlled by a computer over bluetooth Wireless_RemoteControl
- This Program uses a timer to tell if the robot has driven to the other side of the ring CollisionTimer
- This Program finds the other robot in a ring for reset purposes by waiting on the edge of the ring FindPartnerPassive
- This Program finds the other robot in a ring for reset purposes by driving into the other robot FindPartnerActive
- This Program lets the robot drive around the edge of a zumo ringLine_Follower
- This program lets the robot know how to tell the difference between what region it is on MatchCalibrate
- This Program incorporates a button to simulate how a wireless network would work in a zumo match MatchFull
- This program allows the robot toplay a simple zumo match MatchSimple
- This Program simulates a zumo matfch, including knowing who lost Complex_Line_Avoider
- This Program allows a robot to stay inside a zumo ring Simple_Line_Avoider
- This program allows the robot to stay inside a zumo ring Simple_Line_Detector
-The Brandeis University Robotics Club
Test from Tim