The Z80 library implements a fast, small and accurate emulator of the Zilog Z80. It emulates all that is known to date about this CPU, including the undocumented behaviors, MEMPTR, Q and the special RESET. It also has the honor of having been the first open-source project to provide full emulation of the interrupt mode 0.
The source code is written in ANSI C for maximum portability and is extensively commented. The aim has been to write a well-structured, easy-to-understand piece of software; something solid and elegant that can stand the test of time with no need for major changes.
This Z80 CPU emulator has a classic design with instruction-level granularity that delivers the best performance, whilst offering a reasonable flexibility to achieve precision down to the T-state level.
Instruction-level granularity implies that, except in a few well-defined cases, the execution of a given instruction cannot stop until all its internal M-cycles have been processed (i.e., instructions are not divided into micro-operations). Moreover, registers are modified only once per instruction and the T-state counter is normally updated after a full instruction has been executed.
That said, instructions, flags, memory accesses, interrupts, clock cycles, etc., are accurately emulated according to the available technical documentation, the findings made after decades of research on the Z80 and electronic simulations. And, of course, the emulator passes the most exhaustive tests written to date, including all three major test suites:
This set of programs is intended to help the emulator authors to reach the desired level of the CPU emulation authenticity. Each of the included programs performs an exhaustive computation using each of the tested Z80 instructions, compares the results with values obtained from a real Sinclair ZX Spectrum 48K with Zilog Z80 CPU, and reports any deviations detected.
Results (v1.0)
 z80full.tap Tests all flags and registers. |
 z80doc.tap Tests all registers, but only officially documented flags. |
|
|
 z80flags.tap Tests all flags, ignores registers. |
 z80docflags.tap Tests documented flags only, ignores registers. |
|
|
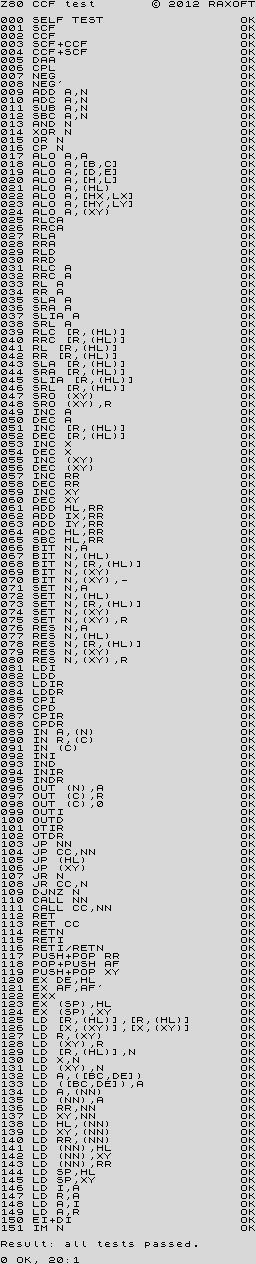
 z80ccf.tap Tests all flags after executing ccf after each instruction tested.
|
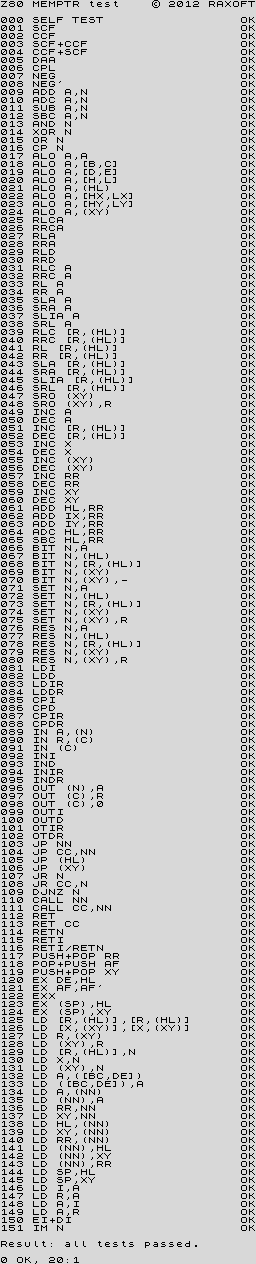
 z80memptr.tap Tests all flags after executing bit N,(hl) after each instruction tested.
|
|
|
Results (v1.2a)
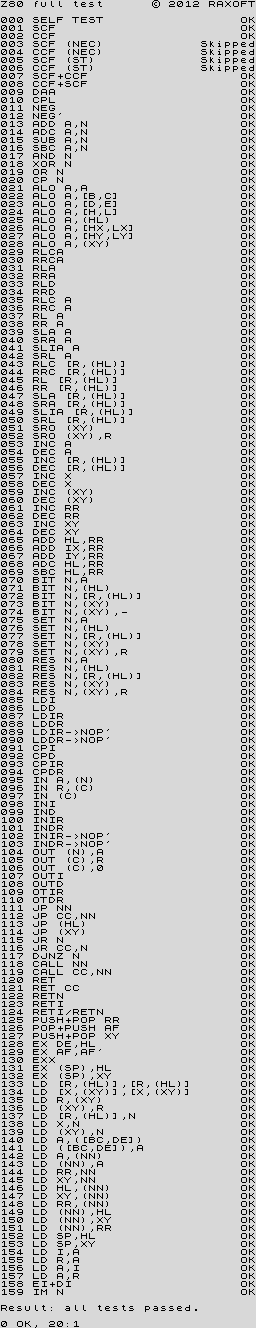
 z80full.tap Tests all flags and registers. |
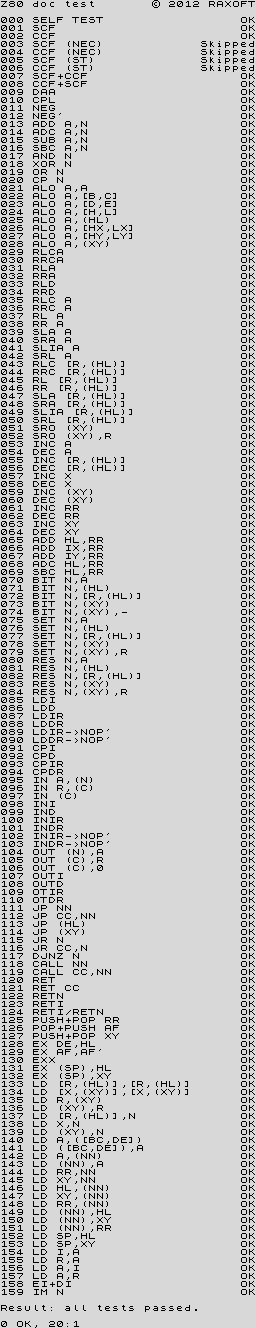
 z80doc.tap Tests all registers, but only officially documented flags. |
|
|
 z80flags.tap Tests all flags, ignores registers. |
 z80docflags.tap Tests documented flags only, ignores registers. |
|
|
 z80ccf.tap Tests all flags after executing ccf after each instruction tested.
|
 z80memptr.tap Tests all flags after executing bit N,(hl) after each instruction tested.
|
|
|
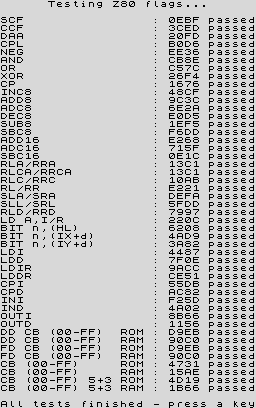
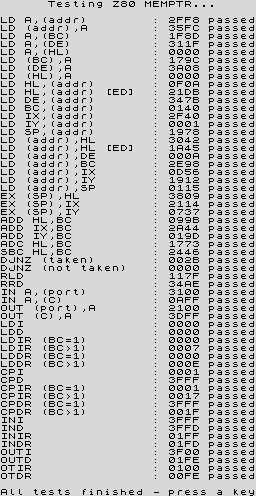
This suite performs a series of tests to verify the MEMPTR documents (English, Russian), which are spot on, as well as a brief run through several of the CBh/DDh/FDh opcode ranges. The test results in the program are compared against those from a NEC D780C-1 CPU, but Simon Conway kindly tested several other Z80 clones, confirming the same results.
Results
 z80tests.tap |
|
|
|
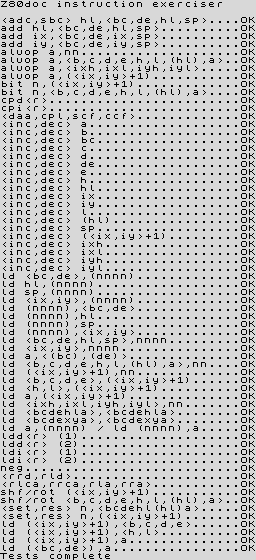
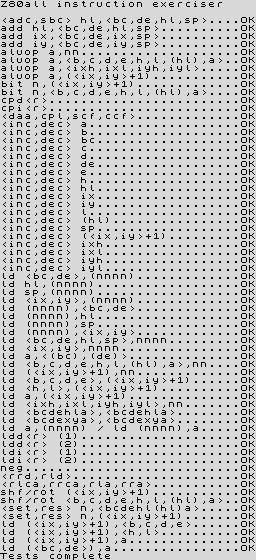
Frank Cringle's Z80 Instruction Set Exerciser attempts to execute every Z80 opcode, putting them through a cycle of tests and comparing the results to actual results from running the code on a real Z80. The exerciser is supplied with Frank's Yaze (Yet Another Z80 Emulator). It is often difficult to track down, so Jonathan Graham Harston put it together here, as well as some conversions. The latest release of Yaze is available at Andreas Gerlich's website.
Results (Jonathan Graham Harston's version)
 zexdoc.tap Tests officially documented flag effects. |
 zexall.tap Tests all flag changes. |
|
|
Results (Jan Bobrowski's version)
 zexfix.tap Tests all flag changes. |
 zexbit.tap Tests all flag changes of the bit instructions.
|
|
|
Results (Patrik Rak's version)
 zexall2.tap |
|
First, add the zxe repository and update the package index:
sudo mkdir -pm700 /root/.gnupg
sudo mkdir -pm755 /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring /etc/apt/keyrings/zxe-archive-keyring.gpg --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv-keys FE214A38D6A0C01D9AF514EE841EA3BD3A7E1487
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/zxe-archive-keyring.gpg] https://zxe.io/repos/apt stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/zxe.list
sudo apt updateNext, install the library package:
sudo apt install libz80In case you need to build software that requires the Z80 library, install the development package too:
sudo apt install libz80-devFirst, add and sync the zxe overlay:
eselect repository add zxe git https://github.com/redcode/zxe-gentoo-overlay.git
emaint sync --repo zxeThen install the library:
emerge emulation-libs/z80brew install redcode/zxe/z80Pre-built binaries for Windows are available on the download page.
You will need CMake v3.14 or later to build the package and, optionally, recent versions of Doxygen, Sphinx and Breathe to compile the documentation. Also, make sure that you have LaTeX with PDF support installed on your system if you want to generate the documentation in PDF format.
The Z80 library requires some types and macros included in Zeta, a header-only, dependency-free library used for portability reasons. Install Zeta or extract its source code tarball to the root directory of the Z80 project or its parent directory. Zeta is the sole dependency; the emulator does not depend on the C standard library.
Lastly, the package includes two testing tools, which are optional to build. The first one runs various Z80-specific tests for CP/M and ZX Spectrum, and will use libzip and zlib if they are available on your system. The second tool is for unit tests in JSON format and requires the cJSON and Z80InsnClock libraries.
Once the prerequisites are met, create a directory and run cmake from there to prepare the build system:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake [options] <Z80-project-directory>The resulting build files can be configured by passing options to cmake. To show a complete list of those available along with their current settings, type the following:
cmake -LAH -N -B .If in doubt, read the CMake documentation for more information on configuration options. The following are some of the most relevant standard options of CMake:
-
Generate shared libraries rather than static libraries.
The default isNO. -
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=(Debug|Release|RelWithDebInfo|MinSizeRel)
Choose the type of build (configuration) to generate.
The default isRelease. -
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_NAME_DIR="<path>"
Specify the directory portion of the dynamic library install name on Apple platforms (for installed shared libraries).
Not defined by default. -
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX="<path>"
Specify the installation prefix.
The default is"/usr/local"(on UNIX and UNIX-like operating systems).
Package-specific options are prefixed with Z80_ and can be divided into two groups. The first one controls aspects not related to the source code of the library:
-
-DZ80_DEPOT_LOCATION="<location>"
Specify the directory or URL of the depot containing the test files (i.e., the firmware and software required by thetest-Z80tool).
The default is"http://zxe.io/depot". -
-DZ80_FETCH_TEST_FILES=(YES|NO)
IfZ80_WITH_TESTING_TOOLisYES, copy or download the test files from the depot to the build directory.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_INSTALL_CMAKEDIR="<path>"
Specify the directory in which to install the CMake config-file package.
The default is"${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}/cmake/Z80". -
-DZ80_INSTALL_PKGCONFIGDIR="<path>"
Specify the directory in which to install the pkg-config file.
The default is"${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}/pkgconfig". -
-DZ80_NOSTDLIB_FLAGS=(Auto|"[<flag>[;<flag>...]]")
Specify the linker flags used to avoid linking against system libraries.
The default isAuto(autoconfigure flags). If you get linker errors, set this option to"". -
-DZ80_OBJECT_LIBS=(YES|NO)
Build the emulator as an object library.
This option takes precedence overBUILD_SHARED_LIBSandZ80_SHARED_LIBS. If enabled, the build system will ignoreZ80_WITH_CMAKE_SUPPORTandZ80_WITH_PKGCONFIG_SUPPORT, as no libraries or support files will be installed.
The default isNO. -
Build the emulator as a shared library, rather than static.
This option takes precedence overBUILD_SHARED_LIBS.
Not defined by default. -
-DZ80_SPHINX_HTML_THEME="[<name>]"
Specify the Sphinx theme for the documentation in HTML format.
The default is""(use the default theme). -
-DZ80_WITH_CMAKE_SUPPORT=(YES|NO)
Generate and install the CMake config-file package.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_HTML_DOCUMENTATION=(YES|NO)
Build and install the documentation in HTML format.
It requires Doxygen, Sphinx and Breathe.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_PDF_DOCUMENTATION=(YES|NO)
Build and install the documentation in PDF format.
It requires Doxygen, Sphinx, Breathe, and LaTeX with PDF support.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_PKGCONFIG_SUPPORT=(YES|NO)
Generate and install the pkg-config file.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_STANDARD_DOCUMENTS=(YES|NO)
Install the standard text documents distributed with the package:AUTHORS,COPYING,COPYING.LESSER,HISTORY,READMEandTHANKS.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_STEP_TESTING_TOOL=(YES|NO)
Buildstep-test-Z80, a tool for unit tests in JSON format.
It requires cJSON and Z80InsnClock.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_TESTING_TOOL=(YES|NO)
Buildtest-Z80, a tool that runs various Z80-specific tests for CP/M and ZX Spectrum.
The default isNO.
The second group of package-specific options configures the source code of the library by predefining macros that enable optional features:
-
-DZ80_WITH_EXECUTE=(YES|NO)
Build the implementation of thez80_executefunction.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_FULL_IM0=(YES|NO)
Build the full implementation of the interrupt mode 0 rather than the reduced one.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_IM0_RETX_NOTIFICATIONS=(YES|NO)
Enable optional notifications for anyretiorretninstruction executed during the interrupt mode 0 response.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_PARITY_COMPUTATION=(YES|NO)
Enable actual parity calculation for the P/V flag instead of using a table of precomputed values (NOT RECOMMENDED for production builds).
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_PRECOMPUTED_DAA=(YES|NO)
Use a table of precomputed values to emulate thedaainstruction (NOT RECOMMENDED for production builds).
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_Q=(YES|NO)
Build the implementation of Q.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_SPECIAL_RESET=(YES|NO)
Build the implementation of the special RESET.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_UNOFFICIAL_RETI=(YES|NO)
Configure the undocumented instructionsED5Dh,ED6DhandED7Dhasretiinstead ofretn.
The default isNO. -
-DZ80_WITH_ZILOG_NMOS_LD_A_IR_BUG=(YES|NO)
Build the implementation of the bug affecting the Zilog Z80 NMOS, which causes the P/V flag to be reset when a maskable interrupt is accepted during the execution of theld a,{i|r}instructions.
The default isNO.
Package maintainers are encouraged to use at least the following options for the shared library:
-DZ80_WITH_EXECUTE=YES
-DZ80_WITH_FULL_IM0=YES
-DZ80_WITH_IM0_RETX_NOTIFICATIONS=YES
-DZ80_WITH_Q=YES
-DZ80_WITH_ZILOG_NMOS_LD_A_IR_BUG=YES
Finally, once the build system is configured according to your needs, build and install the package:
cmake --build . [--config (Debug|Release|RelWithDebInfo|MinSizeRel)]
cmake --install . [--config <configuration>] [--strip]The --config option is only necessary for those CMake generators that ignore CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE (e.g., Xcode and Visual Studio). Use --strip to remove debugging information and non-public symbols when installing non-debug builds of the shared library.
Use the following to build the emulator as a shared library and install it along with the development files into $HOME/.local:
mkdir work && cd work
git clone https://github.com/redcode/Zeta.git
git clone https://github.com/redcode/Z80.git
cd Zeta
mkdir build && cd build
cmake \
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX="$HOME/.local" \
-DZeta_WITH_CMAKE_SUPPORT=YES \
-DZeta_WITH_PKGCONFIG_SUPPORT=YES \
..
cmake --install . --config Release
cd ../../Z80
mkdir build && cd build
cmake \
-DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=YES \
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_NAME_DIR="$HOME/.local/lib" \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX="$HOME/.local" \
-DZ80_WITH_CMAKE_SUPPORT=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_PKGCONFIG_SUPPORT=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_EXECUTE=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_FULL_IM0=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_IM0_RETX_NOTIFICATIONS=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_Q=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_ZILOG_NMOS_LD_A_IR_BUG=YES \
..
cmake --build . --config Release
cmake --install . --config Release --stripThe package includes a tool called test-Z80 that runs the most relevant CP/M and ZX Spectrum versions of the major test suites. Configure the build system with -DZ80_WITH_TESTING_TOOL=YES to enable its compilation and -DZ80_FETCH_TEST_FILES=YES to download the firmware and software required. Also note that the Z80 library must be built with -DZ80_WITH_Q=YES to be able to pass Patrik Rak's tests.
Once you have built the package, type the following to run all tests:
./test-Z80 -p depot/firmware -p depot/software/POSIX -p "depot/software/ZX Spectrum" -aThe tool supports options and can run the tests individually (type ./test-Z80 -h for help). If you prefer to run all tests through CTest, use this command:
ctest --verbose --build-config (Debug|Release|RelWithDebInfo|MinSizeRel)The complete logs generated by test-Z80 emulating different CPU variants are available here:
Note
The CRC errors in the logs of the NEC NMOS variant are normal and match the values obtained on real hardware. The ST CMOS variant is currently under investigation.
Use the following to build and test the emulator:
mkdir work && cd work
git clone https://github.com/redcode/Zeta.git
git clone https://github.com/redcode/Z80.git
cd Z80
mkdir build && cd build
cmake \
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \
-DZ80_FETCH_TEST_FILES=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_TESTING_TOOL=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_EXECUTE=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_FULL_IM0=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_IM0_RETX_NOTIFICATIONS=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_Q=YES \
-DZ80_WITH_ZILOG_NMOS_LD_A_IR_BUG=YES \
..
cmake --build . --config Release
ctest --verbose --build-config Release build-and-test-Z80.sh
build-and-test-Z80.bat
The Z80 library includes a config-file package for integration into CMake-based projects that must be installed for development. Use find_package to find the Z80 package. This creates the Z80 imported library target, which carries the necessary transitive link dependencies. Optionally, the linking method can be selected by specifying either the Shared or Static component.
Example:
find_package(Z80 REQUIRED Shared)
target_link_libraries(your-target Z80)When not specified as a component, the linking method is selected according to Z80_SHARED_LIBS. If this option is not defined, the config-file uses the type of library that is installed on the system and, if it finds both the shared and the static versions, BUILD_SHARED_LIBS determines which one to link against.
To embed the Z80 library as a CMake subproject, extract the source code tarballs of Zeta and Z80 (or clone their respective repositories) into a subdirectory of another project. Then use add_subdirectory in the parent project to add the Z80 source code tree to the build process (N.B., the Z80 subproject will automatically find Zeta and import it as an interface library).
It is advisable to configure the Z80 library in the CMakeLists.txt of the parent project. This will eliminate the need for the user to specify configuration options for the Z80 subproject through the command line when building the main project.
Example:
set(Z80_SHARED_LIBS NO CACHE BOOL "")
set(Z80_WITH_Q YES CACHE BOOL "")
set(Z80_WITH_ZILOG_NMOS_LD_A_IR_BUG YES CACHE BOOL "")
add_subdirectory(dependencies/Z80)
target_link_libraries(your-target Z80)It is important to set the Z80_SHARED_LIBS option. Otherwise, CMake will build the library type indicated by BUILD_SHARED_LIBS, which may not be the desired one.
The source code of the emulator can be configured at compile time by predefining a series of macros. Both Z80.h and Z80.c obey the first two explained below. The rest of the macros are only relevant when compiling Z80.c:
-
#define Z80_EXTERNAL_HEADER "header-name.h"
Specifies the only external header to#include, replacing all others.
Predefine this macro to provide a header file that defines the external types and macros used by the emulator, thus preventing your project from depending on Zeta. You can use this when compilingZ80.cwithin your project or (if your types do not break the binary compatibility) when including<Z80.h>and linking against a pre-built Z80 library. -
#define Z80_STATIC
Indicates that the emulator is a static library.
This macro must be predefined when buildingZ80.cas a static library. Additionally, if you compileZ80.cdirectly within your project or link your program against the static version of the Z80 library, ensure that this macro is defined before including"Z80.h"or<Z80.h>. -
#define Z80_WITH_LOCAL_HEADER
TellsZ80.cto#include "Z80.h"instead of<Z80.h>.
The optional features of the emulator mentioned in the "Configure" section of "Installation from source code" are disabled by default. If you compile Z80.c within your project, enable those features you need by predefining their respective activation macros. They have the same name as their CMake equivalents:
#define Z80_WITH_EXECUTE#define Z80_WITH_FULL_IM0#define Z80_WITH_IM0_RETX_NOTIFICATIONS#define Z80_WITH_PARITY_COMPUTATION#define Z80_WITH_PRECOMPUTED_DAA#define Z80_WITH_Q#define Z80_WITH_SPECIAL_RESET#define Z80_WITH_UNOFFICIAL_RETI#define Z80_WITH_ZILOG_NMOS_LD_A_IR_BUG
Except for Z80_EXTERNAL_HEADER, the above macros can be empty; the source code only checks whether they are defined.
Note
The activation of some of the optional features affects the speed of the emulator due to various factors (read the documentation for more details).
This emulator has been used by the following projects (listed in alphabetical order):
- Augmentinel by Simon Owen ⟩ GitHub
- ceda-cemu by Retrofficina GLG Programs ⟩ GitHub
- CPM-Emulator by Marc Sibert ⟩ GitHub
- f80 by Richard J. Prinz ⟩ GitHub
- Google Capture the Flag (2021) by Google ⟩ GitHub
- King of the Grid by Alex Siryi ⟩ GitHub
- MSX1 Emulator for Raspberry Pi Pico by shippoiincho ⟩ GitHub
- MZ-1500 Emulator for Raspberry Pi Pico by shippoiincho ⟩ GitHub
- MZ-2000/80B Emulator for Raspberry Pi Pico by shippoiincho ⟩ GitHub
- PC-6001mkII Emulator for Raspberry Pi Pico by shippoiincho ⟩ GitHub
- pico-sorcerer-2 by fruit-bat ⟩ GitHub
- pico-zxspectrum by fruit-bat ⟩ GitHub
- RadZ80 by RadAd ⟩ GitHub
- tihle by Peter Marheine ⟩ GitHub · GitLab
- TileMap by Simon Owen ⟩ GitHub
- tranZPUterFusionX by Philip Smart ⟩ GitHub
- Zemu by Jay Valentine ⟩ GitHub · RubyGems
Many thanks to the following individuals (in alphabetical order):
- Akimov, Vadim (lvd)
- For testing the library on many different platforms and CPU architectures.
- azesmbog 🏆
- Banks, David (hoglet) 🏆
- Beliansky, Anatoly (Tolik_Trek)
- For validating tests on real hardware. 1.2
- Bobrowski, Jan
- For fixing the "Z80 Full Instruction Set Exerciser for Spectrum". 7
- boo_boo 🏆
- Brady, Stuart
- For his research on the
ccf/scfinstructions. 12
- For his research on the
- Brewer, Tony 🏆
- Bystrov, Dmitry (Alone Coder)
- For validating tests on real hardware. 1.2
- Chandler, Richard
- For his corrections to the documentation.
- For validating tests on real hardware. 14
- Chunin, Roman (CHRV)
- Conway, Simon (BadBeard)
- For validating the "Z80 Test Suite" on several Z80 clones. 15
- Cooke, Simon 🏆
- For discovering how the
out (c),0instruction behaves on the Zilog Z80 CMOS. 16
- For discovering how the
- Cringle, Frank D.
- For writing the "Z80 Instruction Set Exerciser". 17
- Devic, Goran
- For his research on undocumented behaviors of the Z80 CPU. 18
- Dunn, Paul (ZXDunny)
- For his corrections to the documentation.
- Equinox
- For his corrections to the documentation.
- Flammenkamp, Achim
- For his article on Z80 interrupts. 19
- Gimeno Fortea, Pedro 🏆
- goodboy
- Greenway, Ian
- Harston, Jonathan Graham
- Helcmanovsky, Peter (Ped7g) 🎖️
- Iborra Debón, Víctor (Eremus)
- For validating tests on real hardware.
- icebear
- ICEknight
- For validating tests on real hardware.
- Kladov, Vladimir 🏆
- Krook, Magnus
- For validating tests on real hardware. 1.3
- London, Matthew (mattinx)
- For validating tests on real hardware.
- Martínez Cantero, Ricardo (Kyp)
- For validating tests on real hardware.
- Molodtsov, Aleksandr
- Nair, Arjun
- For validating tests on real hardware. 1
- Nicolás-González, César
- For helping me to investigate the unstable behavior of the
ccf/scfinstructions.
- For helping me to investigate the unstable behavior of the
- Ortega Sosa, Sofía
- For optimizing the emulator.
- For her support.
- Owen, Simon
- For the idea of the hooking method used in this emulator.
- Ownby, Matthew P.
- For his research on the state of the registers after POWER-ON. 29
- Rak, Patrik 🏆
- Rodríguez Jódar, Miguel Ángel (mcleod_ideafix)
- For his research on the state of the registers after POWER-ON/RESET. 32
- Rodríguez Palomino, Mario (r-lyeh)
- For teaching me how emulators work.
- Sainz de Baranda y Romero, Manuel
- For teaching me programming and giving me my first computer.
- Sánchez Ordiñana, José Ismael (Vaporatorius)
- Sevillano Mancilla, Marta (TheMartian)
- For validating tests on real hardware. 14.1
- Stevenson, Dave
- Titov, Andrey (Titus)
- Vučenović, Zoran
- For writing the Pascal binding.
- Weissflog, Andre (Floh) 🏆
- Wilkinson, Oli (evolutional)
- For validating tests on real hardware. 1
- Wlodek
- Woodmass, Mark (Woody) 🎖️
- Young, Sean 🏆
- ZXGuesser
- For validating tests on real hardware.
- https://spectrumcomputing.co.uk/forums/viewtopic.php?t=6102
- https://zx-pk.ru/threads/34173-revers-inzhiniring-z80.html
- https://zx-pk.ru/threads/35936-zagadka-plavayushchikh-flagov-scf-ccf-raskryta!.html
- https://stardot.org.uk/forums/viewtopic.php?t=15464
- Banks, David (2018-08-21). "Undocumented Z80 Flags" rev. 1.0.
- https://github.com/hoglet67/Z80Decoder/wiki/Unstable-CCF-SCF-Behaviour
- http://wizard.ae.krakow.pl/~jb/qaop/tests.html
- https://zxpress.ru/zxnet/zxnet.pc/5909
- https://zx-pk.ru/threads/2506-komanda-bit-n-(hl).html
- https://zx-pk.ru/threads/2586-prosba-realshchikam-ot-emulyatorshchikov.html
- boo_boo; Kladov, Vladimir (2006-03-29). "MEMPTR, Esoteric Register of the Zilog Z80 CPU".
- https://sourceforge.net/p/fuse-emulator/mailman/message/6929573
- Brewer, Tony (2014-12). "Z80 Special Reset".
- https://spectrumcomputing.co.uk/forums/viewtopic.php?t=10555
- https://worldofspectrum.org/forums/discussion/20345
- https://groups.google.com/g/comp.os.cpm/c/HfSTFpaIkuU/m/KotvMWu3bZoJ
- Cringle, Frank D. (1998-01-28). "Yaze - Yet Another Z80 Emulator" v1.10.
- ftp://ftp.ping.de/pub/misc/emulators/yaze-1.10.tar.gz
- https://baltazarstudios.com/zilog-z80-undocumented-behavior
- Flammenkamp, Achim. "Interrupt Behaviour of the Z80 CPU".
- Young, Sean (1998-10). "Z80 Undocumented Features (in Software Behaviour)" v0.3.
- https://elmundodelspectrum.com/desenterrando-el-primer-emulador-de-spectrum
- https://elmundodelspectrum.com/con-vosotros-el-emulador-de-pedro-gimeno-1989
- https://sourceforge.net/p/fuse-emulator/mailman/message/4502844
- Harston, Jonathan Graham (2008). "Full Z80 Opcode List Including Undocumented Opcodes" v0.11 (revised).
- Harston, Jonathan Graham (2012). "Z80 Microprocessor Undocumented Instructions" v0.15.
- Harston, Jonathan Graham (2014). "Z80 Opcode Map" v0.10 (revised).
- https://mdfs.net/Software/Z80/Exerciser/Spectrum
- https://github.com/MrKWatkins/ZXSpectrumNextTests
- Young, Sean (2005-09-18). "Undocumented Z80 Documented, The" v0.91.
- https://worldofspectrum.org/forums/discussion/41704
- https://worldofspectrum.org/forums/discussion/41834
- https://worldofspectrum.org/forums/discussion/34574
- https://jisanchez.com/test-a-dos-placas-de-zx-spectrum
- Weissflog, Andre (2021-12-17). "New Cycle-Stepped Z80 Emulator, A".
- https://github.com/floooh/v6502r
- https://groups.google.com/g/comp.sys.sinclair/c/WPsPr6j6w5k/m/O_u1zNQf3VYJ
- Young, Sean (1997-09-21). "Zilog Z80 CPU Specifications".
Copyright © 1999-2025 Manuel Sainz de Baranda y Goñi.
This library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License along with this library. If not, see https://www.gnu.org/licenses/.
Projects where the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License prevent the use of this library, or require unwanted publication of the source code of commercial products, may apply for a special license.




