skiplist is a simple skip list implementation in Go. It stores data in a key value manner. The key is of type string, and the value is a byte array.
A skip list is a probabilistic data structure that allows
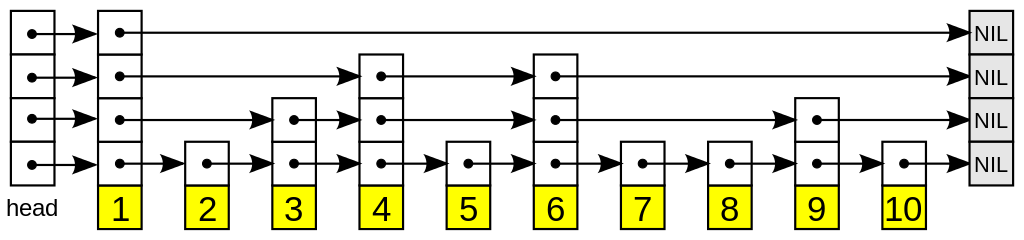
In layman's terms, a skip list is a data structure that looks like a linked list and has sorted elements. A node could span to higher levels. Levels are used to make searching faster. Searching is done by checking if the current node's key is smaller. If it is smaller, it will skip it. Else, it will go down a level. Notice that not all node spans to the highest level, so the search can be done by skipping nodes that are not needed to be checked. Hence the name skip list. The generation of a node's level depends on a random number, hence the probabilistic feature.
Try the skip list in your Go program by running
go get github.com/godlixe/skiplist
and importing github.com/godlixe/skiplist on the top of your program.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/godlixe/skiplist"
)
func main() {
// creates a new skiplist with max level of 10
list := skiplist.New(10)
// sets the key "a" to store the byte array value of "hi"
list.Set("a", []byte("hi"))
// search the list for the key "a"
res, err := list.Search("a")
// prints the result
fmt.Println(string(res), err)
// update the key "a" to store the byte array value of "hello"
list.Set("a", []byte("hello"))
res, err = list.Search("a")
fmt.Println(string(res), err)
// delete key "a" from the list
list.Delete("a")
res, err = list.Search("a")
fmt.Println(string(res), err)
}