- c의 기본 문법들을 실습해본다.
-
\n : new line (goto next line and move first column)
-
\r : carraige return (goto first column of line)
-
\t : tab (same as space 8)
-
\b : back
-
\a : alarm
-
\0 : null (end of string)
-
문자열에서 '' 표시는 special character의 시작을 알리는 기호이다.
-
special character로 cursor의 위치만 제어한다.
- 10진법의 경우는 일반 정수형으로 쓰면된다.
- 8진법의 경우는 10진법 표기법 앞에 0을 붙인다.
- 16진법의 경우는 숫자 앞에 0x를 붙인다.
예를 들자면 다음과 같다.
-
0101 ==> 8^2 + 1 = 64 + 1 = 65
-
8진법 0101을 10진법으로 고쳤다.
-
0x1A ==> 1*16^1 + 10 = 26
-
16진법 수를 10진법 수로 바꾸었다.
- 문자열(string)은 double quotation mark(" ") 로 감싼다.
- 문자(char)는 single quotation mark(' ')로 감싼다.
- scanf 함수를 사용하여 입력을 받을 때 사용하는 지시자들이다.
- %d : decimal value
- %i : integer value
- %u, %o, %x : unsigned int value (decimal, octa-decimal, hexadecimal)
- %c : character
- %s : string(character array)
- %p : pointer value(address value)
- %f : float value
- %lf : double value
-
printf 함수를 사용하여 출력할 때 사용하는 문자 포맷 지시자들이다.
-
%d : decimal value
-
%c : single character
-
%s : string(character array)
-
%u : unsigned int
-
%lu : unsinged long int
-
%llu : unsigned long long int
-
%f : float or double
-
%.3f : print number of float or double decimal with precision 3.
-
%10.2f : print 10 character with precision 2 (include .)
-
%010.2f : print 10 character with precision 2 (include .)
-
%p : print value of pointer p
-
%x : print value with format hexadecimal
-
%o : print value with format octal decimal
-
example
-
printf("%10.2f \n", 123.4567); // [ 123.45]
-
printf("%010.2f \n, 123.4567); // [0000123.45]
-
# option means numeral system
-
example
-
printf("%d, %#x, %#o", 100, 100, 100); // printed as 100, 0x64, 0144
- ascii code는 7비트를 통해 코드표의 모든 문자를 표현할 수 있다. 컴퓨터 초기에 사용했던 방식이다.
- ASCII Code에 속한 문자 하나는 1바이트를 차지한다. (여분의 1비트는 parity bit이다.)
- 현대 컴퓨팅 시스템은 UTF-X 방식을 주로 사용한다.
- Integer Type : char(1B), short int(2B), int(4B) long int(4B), long long int(8B)
- Real number Type : float(4B), double (8B), long double(8B)
- int(4B) : -2,147,483,648 ~ 2,147,483,647 (10자리 표현)
- short int(2B) : -32,768 ~ 32,767 (5자리 표현)
- signed long int(4B) : -2,147,483,648 ~ 2,147,483,647 (10자리 표현)
- unsigned long int(4B) : 0 ~ 4,294,967,295 (10자리 표현)
- signed long long int(8B) : -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 ~ 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 (19자리 표현)
- unsigned long long int(8B) : 0 ~ 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 (20자리 표현)
-
unsigned int : 100u, 100U
-
singed long int : 100l, 100L
-
unsigned long int : 100ul, 100UL
-
signed long long int : 100ll
-
unsigned long long int : 100ull, 100ULL
-
char, short는 별도 타입을 의미하는 suffix가 없다.
-
float : 3.5f, 3.5F
-
double : 3.5
-
long double : 3.5l, 3.5L
- 다양한 컨벤션이 있으므로, 조직의 규칙을 따른다.
- 하지만 기본적으로 지켜야할 규칙들이 있다.
- 특수문자 금지.( 언더바 _ 가능, 하지만 가급적 쓰지 말것. )
- 첫부분에 숫자 금지.
- 예약어 사용 금지
- 명사와 명사 연결시 연산자(+,-,*,/) 금지.
#include <stdio.h>
- printf : print string with format
- scanf : scan string with format
- gets : 공백을 포함해서 enter가 눌러질 때까지 입력받아 배열에 저장. 엔터키가 입력되면, 엔터 문자를 \0으로 바꿔서 맨 끝에 추가후 저장.
- getchar : 입력 후 엔터가 필요. scanf에 %c로 한 글자를 받는 것과 동일.
- putchar : 한 글자를 출력하는 함수.
#include <conio.h>
-
getch : 엔터 없이 한 글자를 입력 받으며 화면에 입력한 글자는 안보임.
-
putch : 한 글자를 출력하는 함수.
-
fflush(stdin) : 이전에 들어가 있던 값들이 전부 저장된 후, 버퍼를 청소한다.
Arithmetic operator
- + - & /
Modulus operator
- % (get remainder)
Assignment
- =
Unary operator
- & : address of
- * : value of address
example
- +a, -b, sizeof a, &a,
Binary operator
- %, +, -
- % 연산자의 경우, 피연산자가 모두 양의 정수여야 한다.(음수 일 경우, 컴파일러 의존적. 오류발생가능성 존재.)
example
- a+b, a-b
** Compound assignment operator**
- 변수 초기화에 조심.
- 복합연산자는 연산의 횟수를 줄여준다.
- 복합연산자에서 우변의 연산이 우선이다.
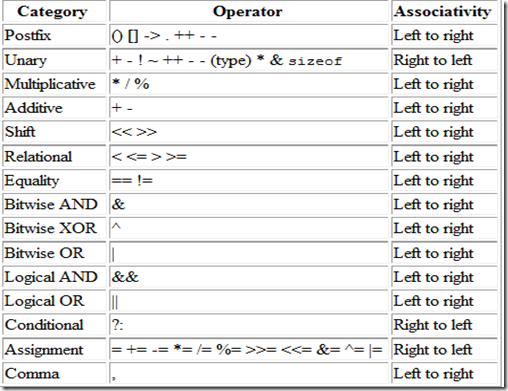
- -=, +=, /=, *=
- 연산자는 우선순위가 있다.
example
- a /= a - b + 1;
- a %= b -= 3;
Prefix / Postfix Operators
- Prefix operator : 전치 연산자. 연산자가 우선적으로 계산된다.
- Postfix operator : 후치 연산자. 연산자가 가장 나중에 적용된다.
- 연산의 종료의 기준은 ; 표시이다.
example
- b = a++ + 10; // 모든 연산자(=, +)가 평가된 후, ; 를 벗어나면 ++ 연산자가 적용됨.
- b = ++a + 10; // ++ 연산자가 먼저 평가 된 후, 나머지 연산자가 평가됨.
- if(a++){}; // 후치연산자 ++은 if의 ( )를 벗어난 후, 값이 평가된다.
example
int a=1, b=2, c=3;
a = -3*-4%+6/5; // ==> a = ((((-3)*(-4))%(+6))/5);
a += b - c *= 2; // ==> a += (b - c) *= 2; ==> a += -1 *= 2; // l-value error
a += b -= c *= 2; // ==>
- Call by address : 변수의 주소를 전달한다.
- Call by value : 변수의 값을 저장.
- 키보드에서 값이 입력되면, 그 값들이 바로 ram으로 적재되어서 cpu에서 연산 후, 값이 평가되어 담기는게 안니다.
- 구조를 간단히 그려보자면 다음과 같다.
- CPU - Keyboard_Buffer - User Input
- 이런 다이어그램을 그릴 수 있다.
- 키보드의 입력이 끝난 후, 엔터를 치면, 버퍼의 값들이 전부 ram으로 적재된다.