给定一棵二叉树的根 root,请你考虑它所有 从根到叶的路径:从根到任何叶的路径。(所谓一个叶子节点,就是一个没有子节点的节点)
假如通过节点 node 的每种可能的 “根-叶” 路径上值的总和全都小于给定的 limit,则该节点被称之为「不足节点」,需要被删除。
请你删除所有不足节点,并返回生成的二叉树的根。
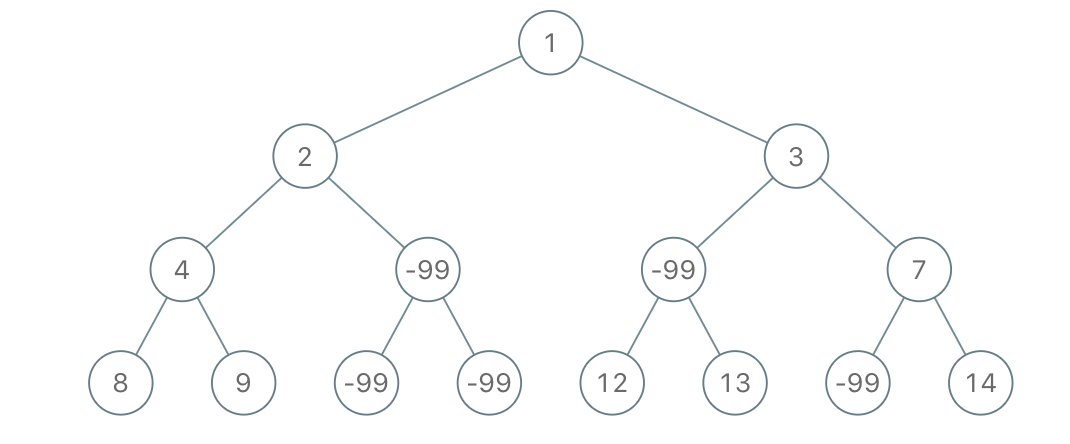
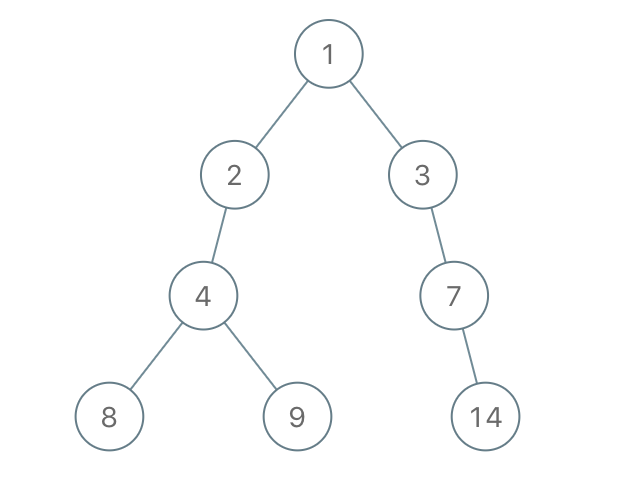
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,-99,-99,7,8,9,-99,-99,12,13,-99,14], limit = 1
输出:[1,2,3,4,null,null,7,8,9,null,14]
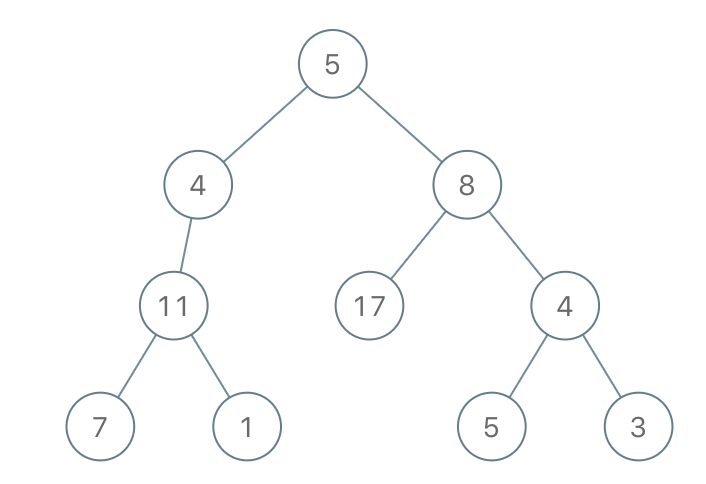
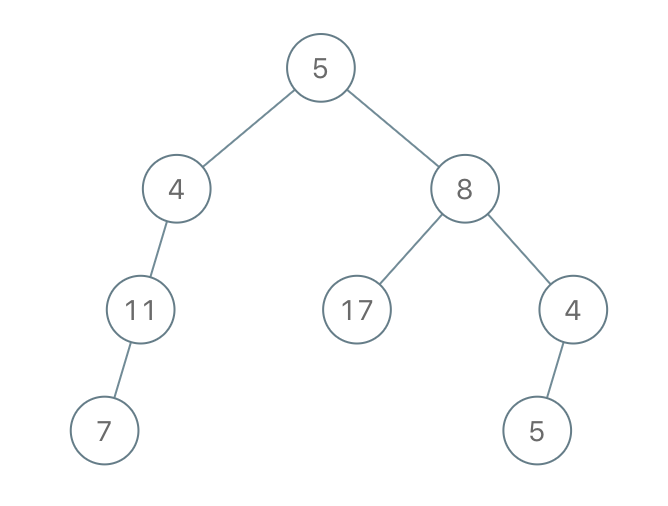
示例 2:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,17,4,7,1,null,null,5,3], limit = 22
输出:[5,4,8,11,null,17,4,7,null,null,null,5]
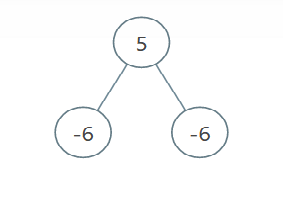
示例 3:
输入:root = [5,-6,-6], limit = 0 输出:[]
提示:
- 给定的树有
1到5000个节点 -10^5 <= node.val <= 10^5-10^9 <= limit <= 10^9
方法一:递归
递归遍历整棵树,如果到达叶子结点且路径和小于 null 表示删除。如果左右子树都被删除,说明经过当前结点的路径和也一定小于
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def sufficientSubset(
self, root: Optional[TreeNode], limit: int
) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None:
return None
limit -= root.val
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
return None if limit > 0 else root
root.left = self.sufficientSubset(root.left, limit)
root.right = self.sufficientSubset(root.right, limit)
return None if root.left is None and root.right is None else root/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sufficientSubset(TreeNode root, int limit) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
limit -= root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return limit > 0 ? null : root;
}
root.left = sufficientSubset(root.left, limit);
root.right = sufficientSubset(root.right, limit);
return root.left == null && root.right == null ? null : root;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sufficientSubset(root *TreeNode, limit int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
limit -= root.Val
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
if limit > 0 {
return nil
}
return root
}
root.Left = sufficientSubset(root.Left, limit)
root.Right = sufficientSubset(root.Right, limit)
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return nil
}
return root
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sufficientSubset(TreeNode* root, int limit) {
if (!root) return nullptr;
limit -= root->val;
if (!root->left && !root->right) return limit > 0 ? nullptr : root;
root->left = sufficientSubset(root->left, limit);
root->right = sufficientSubset(root->right, limit);
return !root->left && !root->right ? nullptr : root;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} limit
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var sufficientSubset = function (root, limit) {
if (!root) {
return null;
}
limit -= root.val;
if (!root.left && !root.right) {
return limit > 0 ? null : root;
}
root.left = sufficientSubset(root.left, limit);
root.right = sufficientSubset(root.right, limit);
return !root.left && !root.right ? null : root;
};